Here’s the uncomfortable truth: that chronological blog you’ve been feeding for years? It’s scattering your link equity like confetti and sending visitors straight to your competitors. Every new post pushes your best content deeper into the archives, where search engines and humans alike will never find it.
Content hubs flip this model entirely, organizing your expertise into interconnected topic clusters that build authority, keep readers engaged, and actually convert.
This isn’t just a better way to organize content. It’s a fundamentally different content strategy that transforms your website into a destination, rather than a waystation.
TL;DR
- What it is: A centralized destination organizing related content around one topic using strategic internal links—not a chronological blog, but a purposeful hub-and-spoke structure that builds topical authority and guides visitors through connected resources.
- Why it works: Signals expertise to search engines (supports E-E-A-T), passes link equity strategically through internal linking, prevents keyword cannibalization, and increases engagement metrics (time on site, pages per session) while naturally moving visitors through your funnel.
- Four core architectures: Hub-and-Spoke (classic pillar model for SEO), Content Library (filtered browsing), Topic Gateway (deep coverage of one topic), and Content Database (searchable repository for 100+ assets)—choose based on your content volume and goals.
- How to build: Start with keyword research (not gut instinct), audit existing content, create one comprehensive hub page linking to multiple deep-dive spoke pages, master contextual internal linking between hub/spokes, and maintain quarterly with fresh data and new spokes.
- Critical mistakes to avoid: Building without validating search demand, treating it as set-and-forget, using weak generic link blocks instead of contextual links, ignoring mobile optimization (60%+ of traffic), and neglecting E-E-A-T signals especially when using AI-generated content.
What Is a Content Hub? (And What It Definitely Isn’t)
A content hub is a centralized destination that organizes related content around a specific topic or theme, using strategic internal links to guide visitors through interconnected resources. Think of it as your website’s command center for a particular subject—where every piece of content has a purpose and a clear path to the next.
Here’s what makes it different from everything else cluttering your content landscape:
- Not a blog. Blogs list posts chronologically (newest first). Content hubs are organized strategically by topic, intent, and relationship. Your most valuable content doesn’t get buried by last Tuesday’s post about industry trends.
- Not a resource library. Resource centers are essentially digital filing cabinets—they collect assets but don’t necessarily connect them in a meaningful way. A content hub creates a narrative journey through related subtopics.
- Not a category page. Category pages group content by tags. Content hubs establish authority through a hub-and-spoke architecture, featuring a central pillar page supported by in-depth subtopic pages.
The core promise? When someone lands on your content hub, they find everything they need about that topic without bouncing to Wikipedia pages or your competitors. According to HubSpot, companies that blog regularly generate 67% more leads than those that don’t—but those leads multiply when content is strategically organized rather than chronologically scattered.
The Two Different Meanings of “Content Hub” (Yes, Really)
Here’s where things get confusing: “content hub” refers to both a marketing strategy AND a software category. Let’s untangle this.
Content Hub as Marketing Strategy
This is the hub-and-spoke model you’ve probably heard about—a topic authority framework where you create one comprehensive hub page that links out to multiple detailed spoke pages covering related subtopics. It’s pure content marketing structure, focused on SEO-first internal linking architecture and evergreen content organization.
The best part? This strategy costs exactly zero dollars. You can build it with whatever CMS you’re already using.
Content Hub as Software Platform
This is where tools like HubSpot Content Hub, Sitecore Content Hub, Adobe Experience Manager, and ON24 come in. These are content management platforms that help you organize, distribute content, and manage your entire content lifecycle across digital marketing channels. Think digital asset management (DAM), content marketing platform (CMP), and marketing resource management (MRM) rolled into one.
Some brands need the software. Most should start with the strategy.
The 4 Core Content Hub Architectures
Not all content hubs are built the same. Here’s how to choose your blueprint:
1. Hub-and-Spoke (The Classic Hub Pillar Model)
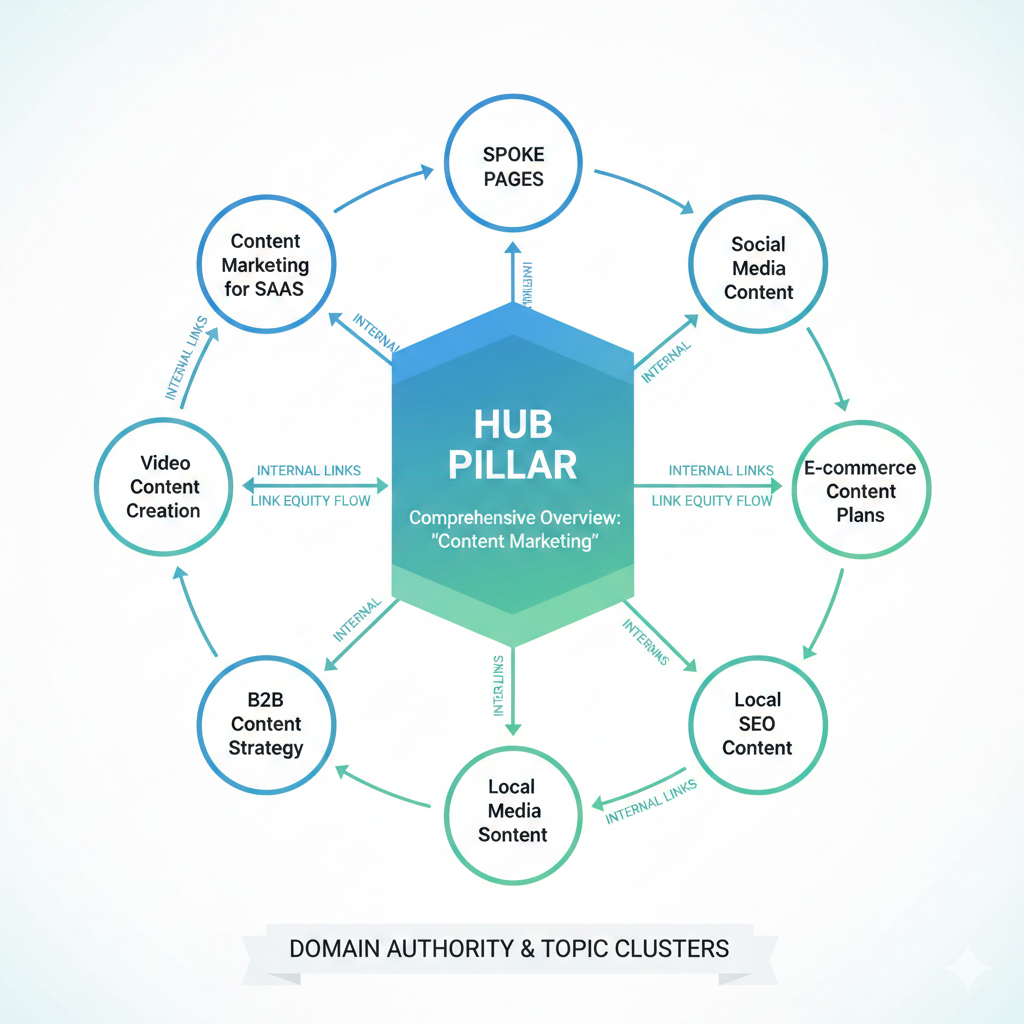
What it is: One central pillar page providing a comprehensive overview, with detailed spoke pages covering specific angles of the topic.
Best for: Building domain authority in a specific subject area, especially when you want to dominate topic clusters in search engines.
How it works: Your hub page targets a broad keyword (like “content marketing”), while spoke pages target long-tail variations (“content marketing for SaaS” or “B2B content strategy”). Strategic internal links flow from hub to spokes and back again, passing link equity and keeping readers exploring.
Real example: Healthline’s medical sites use this perfectly—their main page on “Diabetes” links to subtopic pages about symptoms, treatments, diet, and complications.
2. Content Library (Index-Based Organization)
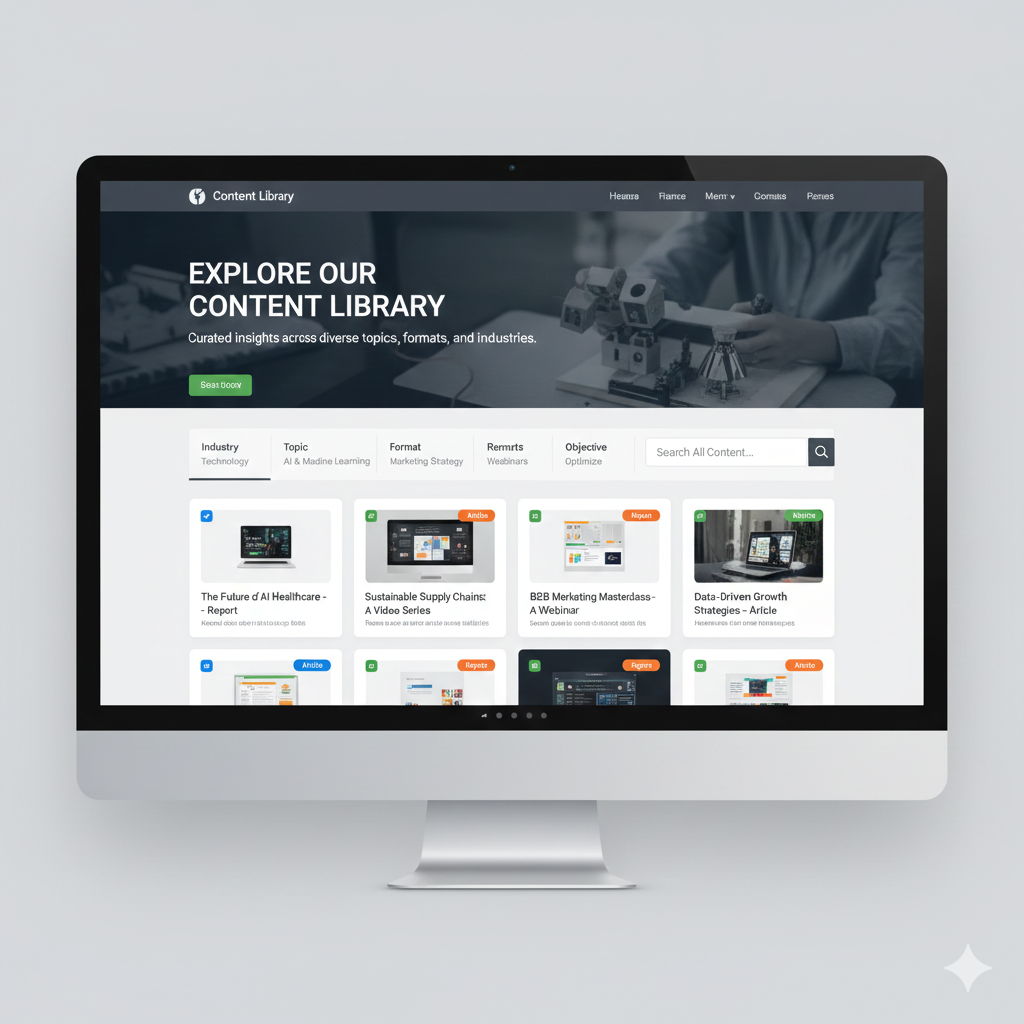
What it is: A structured landing page that organizes diverse topics, formats, and content ideas across your marketing assets—more like a curated museum than a single exhibition.
Best for: Brands with high content volume across multiple themes, especially when serving different target audiences or publishing various content formats (articles, videos, webinars, reports).
How it works: Categories, filters, and search functionality help visitors find exactly what they need. Think of Think With Google’s content library format—you can filter by industry, topic, format, and objective.
3. Topic Gateway (Deep Coverage Model)
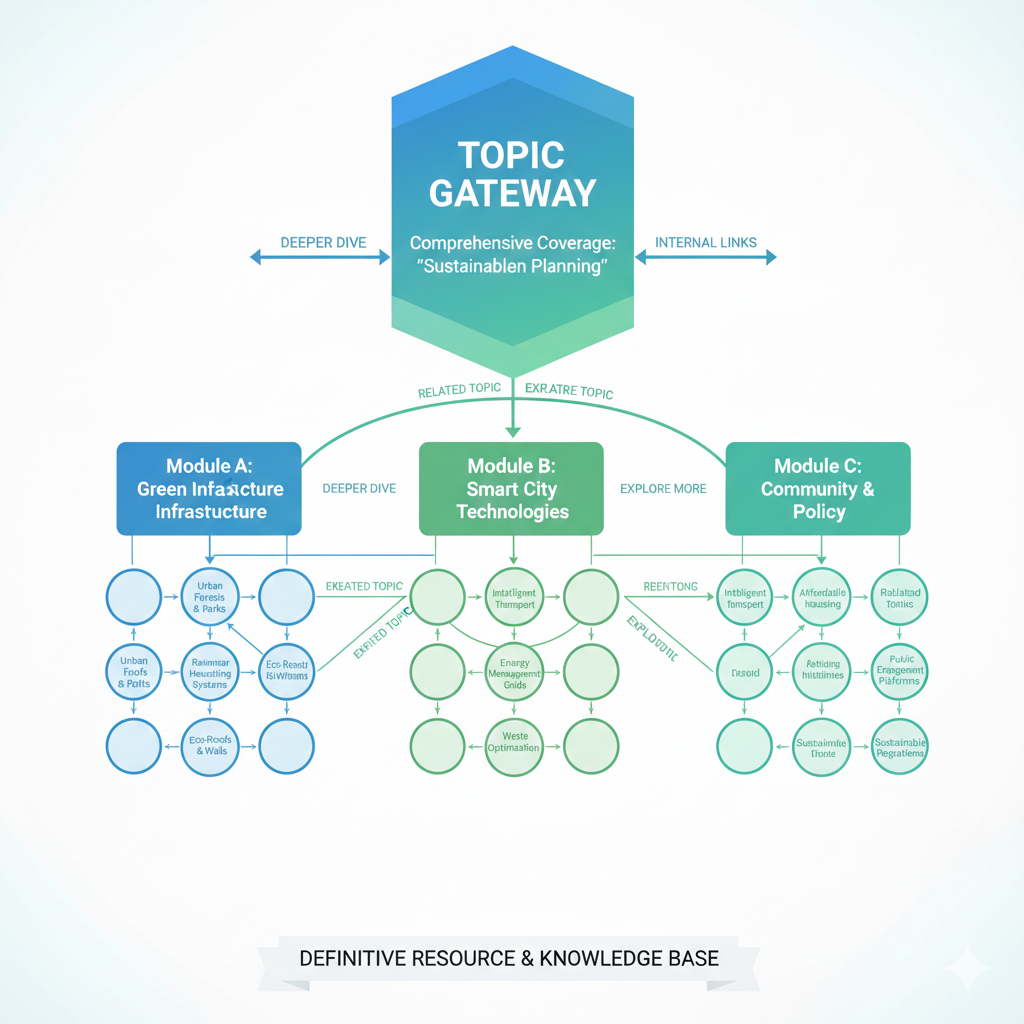
What it is: Comprehensive coverage of one complex subject, going deeper than wider. These topic gateways serve as the definitive resource for a single theme.
Best for: Educational content, knowledge bases, or when you want to own ONE topic completely rather than cover many superficially.
How it works: Instead of linking to 20 different subjects, you create exhaustive coverage of one—exploring every angle, question, and application. The navigation encourages visitors to dive deeper into increasingly specific aspects of the same topic.
4. Content Database (Searchable Repository)
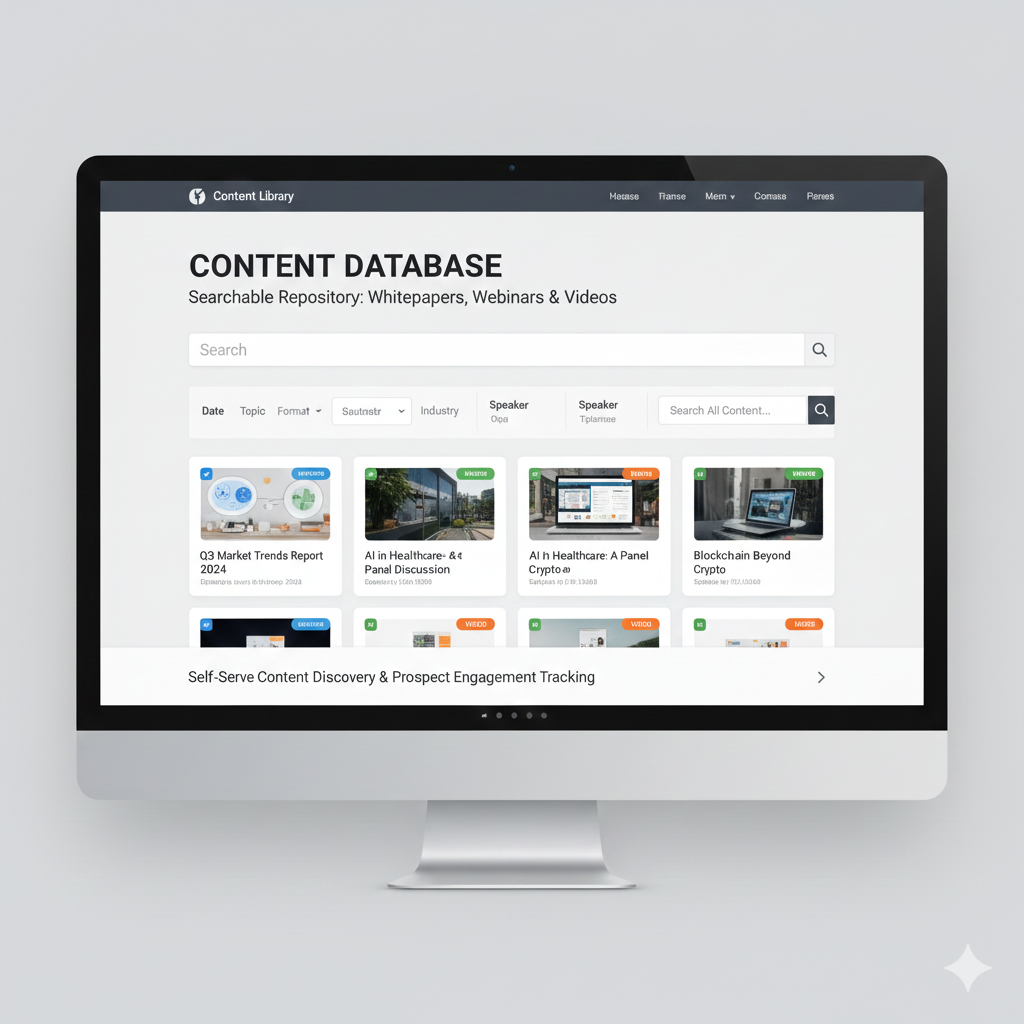
What it is: Filterable, searchable collections of specific digital assets—think webinar libraries, video hubs, or whitepaper collections where discoverability matters more than narrative flow.
Best for: Marketing teams managing hundreds of gated assets, event-driven content, or video-heavy strategies.
How it works: Advanced filtering (by date, topic, format, speaker, or industry) allows users to self-serve. Many B2B brands utilize this approach with downstream applications to track which prospects engage with specific assets.
| Architecture Type | Primary Goal | Navigation Style | Best Content Volume |
| Hub-and-Spoke | SEO authority | Topic clusters | 10-30 pieces |
| Content Library | Multi-topic coverage | Filtered browsing | 50+ pieces |
| Topic Gateway | Deep expertise | Progressive depth | 15-40 pieces |
| Content Database | Asset discovery | Search + filters | 100+ pieces |
Purpose-Driven Hub Taxonomies
Beyond structural architecture, content hubs can be organized by strategic purpose. These purpose-driven models help you align content organization with specific business objectives and audience needs:
Persona-Based Hubs
Content is organized around distinct buyer personas or user roles rather than topics. Each persona gets a dedicated hub tailored to their specific challenges, questions, and journey stage. B2B companies with multiple decision-makers, enterprise software with diverse user roles, or complex sales cycles requiring targeted messaging.
Instead of one “Marketing Automation” hub, you create separate hubs for CMOs, Marketing Directors, and Marketing Coordinators—each addressing role-specific pain points, authority levels, and concerns. Navigation allows users to self-select their persona, and content automatically filters to relevant resources.
Real example: Salesforce organizes content by role (Sales Leader, Marketing Executive, IT Professional) with distinct hubs featuring case studies, challenges, and solutions specific to each persona’s priorities.
Strategic advantage: Higher conversion rates because content speaks directly to the reader’s specific situation, challenges, and decision-making authority.
Campaign-Specific Hubs
Temporary or evergreen content hubs built around specific marketing campaigns, product launches, or seasonal initiatives. Product launches, annual events, seasonal promotions, or integrated marketing campaigns require dedicated landing experiences.
How it works: All campaign assets—blog posts, videos, webinars, case studies, and conversion tools—live in one cohesive hub with campaign-specific branding and messaging. The hub serves as the central destination for all campaign traffic sources (ads, email, social, PR).
Real example: Adobe’s annual Adobe MAX conference hub consolidates session recordings, speaker interviews, product announcements, and follow-up resources in one searchable destination that remains live year-round.
Strategic advantage: Creates a cohesive campaign experience, simplifies promotion (one URL to remember), and extends campaign value beyond the launch window.
Industry-Focused Hubs
Content segmented by vertical market or industry, addressing sector-specific challenges, regulations, and use cases.SaaS platforms serving multiple industries, professional services firms, or any business where industry context dramatically changes the value proposition.

How it works: Your core product or service remains the same, but you create dedicated hubs for Healthcare, Financial Services, Manufacturing, etc.—each featuring industry-specific case studies, compliance guides, terminology, and implementation examples.
Real example: Microsoft Azure maintains separate industry solution hubs for Healthcare, Retail, Financial Services, and Government—each highlighting industry-relevant features, compliance certifications, and customer stories.
Strategic advantage: Demonstrates industry expertise, improves SEO for industry-specific keywords (e.g., “healthcare CRM” vs. generic “CRM”), and increases trust by showing you understand sector-specific challenges.
Format-Driven Hub Taxonomies
When your audience prefers specific content formats or when certain formats drive outsized business results, format-driven hubs make strategic sense:
Video Hubs
Centralized libraries of video content with robust filtering, transcripts, and related resources. Brands with substantial video production, educational platforms, media companies, or businesses where visual demonstration drives conversion.
How it works: Videos are organized by topic, length, series, or speaker with advanced search, bookmarking, and viewing history. Transcripts improve SEO and accessibility. Related written content or CTAs accompany each video.
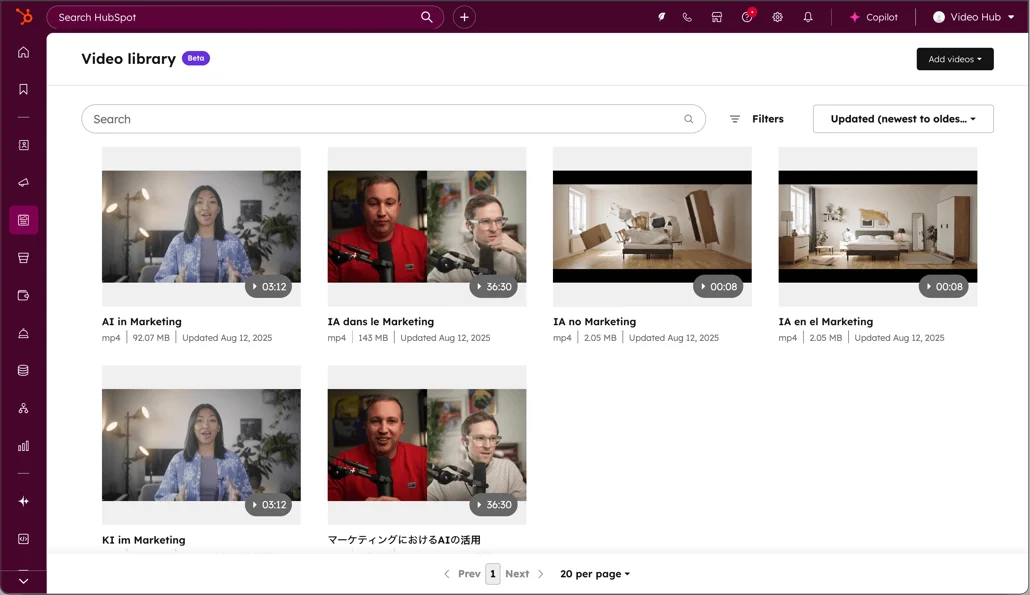
Video content generates 1200% more shares than text and images combined. A dedicated hub maximizes this investment by improving discoverability and watch time.
Learning Hubs (Educational/Academy Model)
What it is: Structured educational experiences with progressive learning paths, skill-based organization, and often certification or completion tracking. SaaS companies offering product training, professional development platforms, or brands positioning as thought leaders through education.
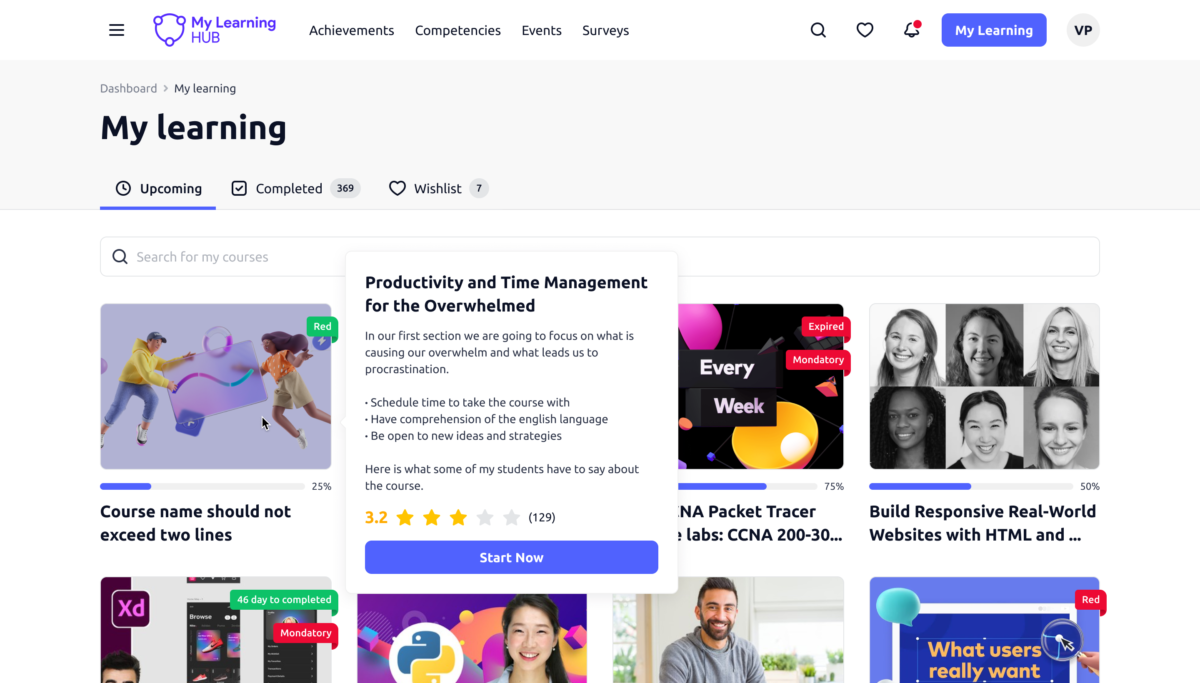
How it works: Content is organized into courses, modules, or learning paths with clear progression. Users can track completion, earn badges/certifications, and return to continue where they left off. Integration with LMS (Learning Management System) platforms adds quizzes, assessments, and user progress tracking.
Educational content builds trust and positions your brand as an authority. Certification programs create networking effects as professionals add credentials to LinkedIn, expanding organic reach.
Webinar Hubs
Dedicated libraries for on-demand webinars, virtual events, and recorded presentations with registration/gating functionality. B2B companies using webinars as primary lead generation tools, event-driven content strategies, or businesses with regular virtual event schedules.
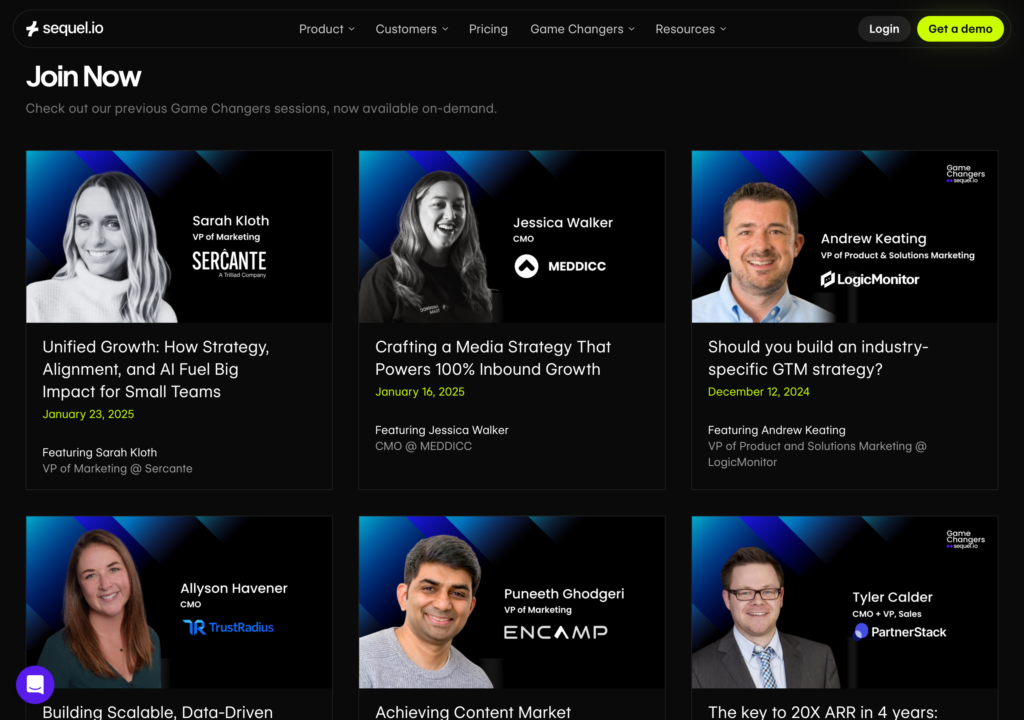
How it works: Upcoming webinars appear with registration CTAs, while past webinars are available on-demand (typically gated). Advanced filtering by date, topic, speaker, or series. Integration with marketing automation platforms triggers nurture sequences based on viewing behavior.
Webinars generate 2-3x higher conversion rates than written content. A dedicated hub maximizes lead capture while extending content lifespan beyond live event dates.
Choosing Your Purpose or Format Model
Ask yourself:
- Do you serve distinctly different audiences? → Persona-Based Hub
- Do you run major campaigns or product launches? → Campaign-Specific Hub
- Do industry-specific concerns dominate buying decisions? → Industry-Focused Hub
- Is video your primary content format? → Video Hub
- Are you building an education-first brand? → Learning Hub
- Do webinars drive your pipeline? → Webinar Hub
Many successful content strategies combine multiple models: a hub-and-spoke structural architecture organized by persona-based purpose with format-specific sub-hubs for video content. The key is choosing models that align with how your audience naturally seeks information and how your business measures success.
Why Content Hubs Actually Matter (Beyond the Buzzword)
Topical Authority That Search Engines Reward
When you publish content scattered across disconnected blog posts, Google sees random articles. When you organize them into a content hub with strong internal links, you’re signaling: “We are the authoritative source on this entire topic.”
This supports E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) in a way that individual posts never can. You’re not just answering one question—you’re demonstrating comprehensive knowledge across a subject cluster.
SEO Performance That Compounds
Here’s the technical advantage: strategic internal linking passes equity throughout your hub, reduces crawl depth, and expands your SERP footprint through keyword clustering. Instead of 15 blog posts competing with each other (keyword cannibalization), you have one authoritative hub ranking for the head term and spokes capturing long-tail variations.
Research from Semrush shows that websites with strong internal linking structures see up to 40% more organic traffic than those without strategic linking.
Engagement Metrics That Actually Move
- Higher time on site (visitors explore related content instead of bouncing)
- More pages per session (the “rabbit hole effect”)
- Lower bounce rates (clear next steps keep people engaged)
Lead Generation Without Being Pushy
The beauty of content hubs? They move visitors naturally through your funnel. Someone researching a topic (awareness stage) reads your hub page, clicks through to a spoke that addresses their specific challenge (consideration), and encounters a relevant CTA for a deeper resource (decision). You’re not interrupting—you’re guiding.
Real Content Hubs You Can Study Right Now
Airbnb’s Locations Hub
Architecture: Hub-and-spoke meets content database
What makes it work: Every major city gets its own hub page with neighborhood guides, travel tips, and property clusters. Internal linking builds massive local SEO authority, while user-generated content keeps everything fresh and trustworthy.
Think With Google

Architecture: Content library
Why it succeeds: Multi-format content (articles, case studies, data reports) organized by industry and objective. It’s a good example of serving multiple target audiences without creating confusion—marketers can filter exactly what they need.
Red Bull’s The Red Bulletin
Architecture: Lifestyle topic gateway
The differentiator: High-production storytelling that positions Red Bull as a media brand, not just an energy drink. The content hub fosters brand affinity through content featuring extreme sports, culture, and adventure, which rarely mentions the product.
B2B Webinar Hubs
Architecture: Content database
Strategy: Gated content behind forms, searchable by topic/speaker/date, with automated email marketing follow-ups. These hubs exist purely for lead capture—and they work because visitors expect to exchange contact info for valuable recorded sessions.
When You Actually Need Content Hub Software (And When You Don’t)
DIY Content Hubs (Free Approach)
What you need: Your existing CMS (WordPress, Webflow, Ghost), time, and a solid internal linking strategy.
Best for: SMBs, startups, content marketing teams under 5 people, or brands with fewer than 50 active content pieces.
Real talk: If you’re publishing 2-4 pieces per month and have basic technical capabilities, you don’t need specialized software. Create a pillar page manually, build your spoke pages, link them strategically, and you’re done.
When Software Makes Sense
You should consider a content marketing platform when:
- Your marketing team manages 500+ digital assets across multiple formats
- You’re distributing content across 5+ channels and need central control
- You require advanced workflow management (approvals, versioning, brand guidelines enforcement)
- You need personalization at scale based on audience segments
- Your content lifecycle involves complex collaboration between multiple teams
Top Content Hub Software Platforms
HubSpot Content Hub
What it does: AI-powered content remixing, brand voice tools, SEO recommendations, and built-in analytics. It’s designed for lead generation first—everything flows toward capturing and nurturing prospects.
Pricing: Free tier available | Starter ~$20/mo | Professional ~$500/mo | Enterprise custom
Best for: Mid-market B2B companies prioritizing lead capture and email marketing integration.
Sitecore Content Hub
- What it does: Enterprise-grade content management, digital asset management, and omnichannel delivery through high-performing GraphQL APIs. Content Hub ONE specifically offers headless architecture for brands that need to publish content across web, mobile, kiosks, and other downstream apps.
- Pricing: Custom enterprise pricing
- Best for: Large organizations managing thousands of marketing assets with complex governance needs.
Adobe Experience Manager
- What it does: Enterprise DAM, workflow automation, multi-site management, and deep integration with Adobe’s marketing stack.
- Pricing: Custom enterprise contracts
- Best for: Fortune 500 brands with massive asset libraries and dedicated marketing teams.
ON24
- What it does: Webinar-centric content hubs, video management, and event-driven digital experience platforms.
- Pricing: Subscription-based, typically $15,000-$50,000/year depending on scale
- Best for: Companies using webinars as primary lead generation tools.
How to Build Your Content Hub (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Pick Your Core Topic Based on Data, Not Gut
Don’t build a content hub around what you think your target audience cares about. Use keyword research to find topic clusters where:
- You have genuine expertise (you can actually create authoritative informational content)
- Search volume exists (people are actively looking for answers)
- Competition is beatable (you’re not fighting WebMD for medical terminology)
- Commercial intent aligns with your brand goals
Tools to use: Semrush, Ahrefs, Google Keyword Planner, or even manual searches to see what “People Also Ask” questions appear.
Step 2: Audit What You Already Have
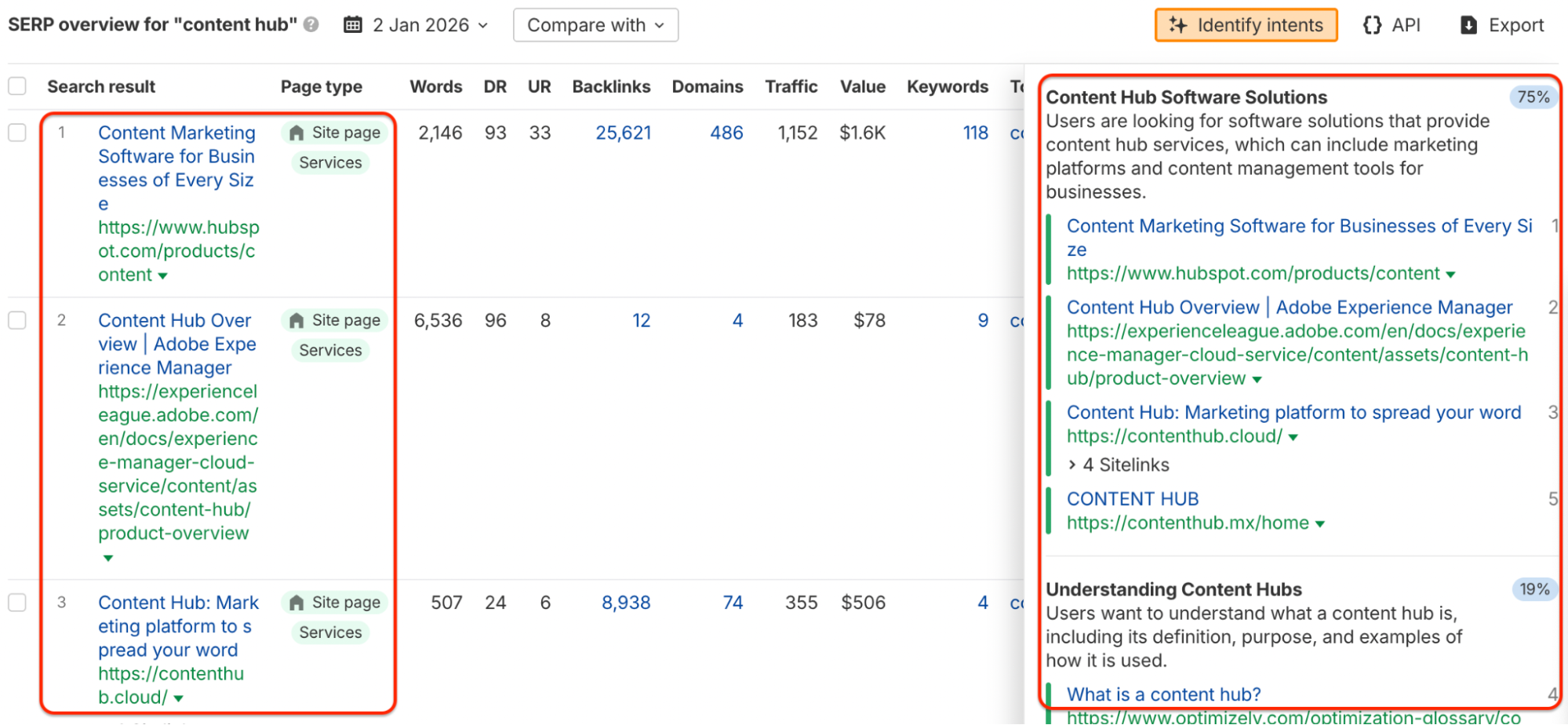
Most brands already have the raw materials for a content hub buried in their blog archives. Run a content audit to:
- Identify existing posts that fit your chosen topic cluster
- Find gaps where you’re missing critical subtopics
- Spot outdated content that needs refreshing
- Determine what to consolidate (merge similar posts to avoid competing with yourself)
Pro move: Look for blog posts that rank on pages 2-3 of Google. These are prime candidates for upgrading into comprehensive spoke pages that link to a new hub.
Step 3: Map Subtopics to Search Intent
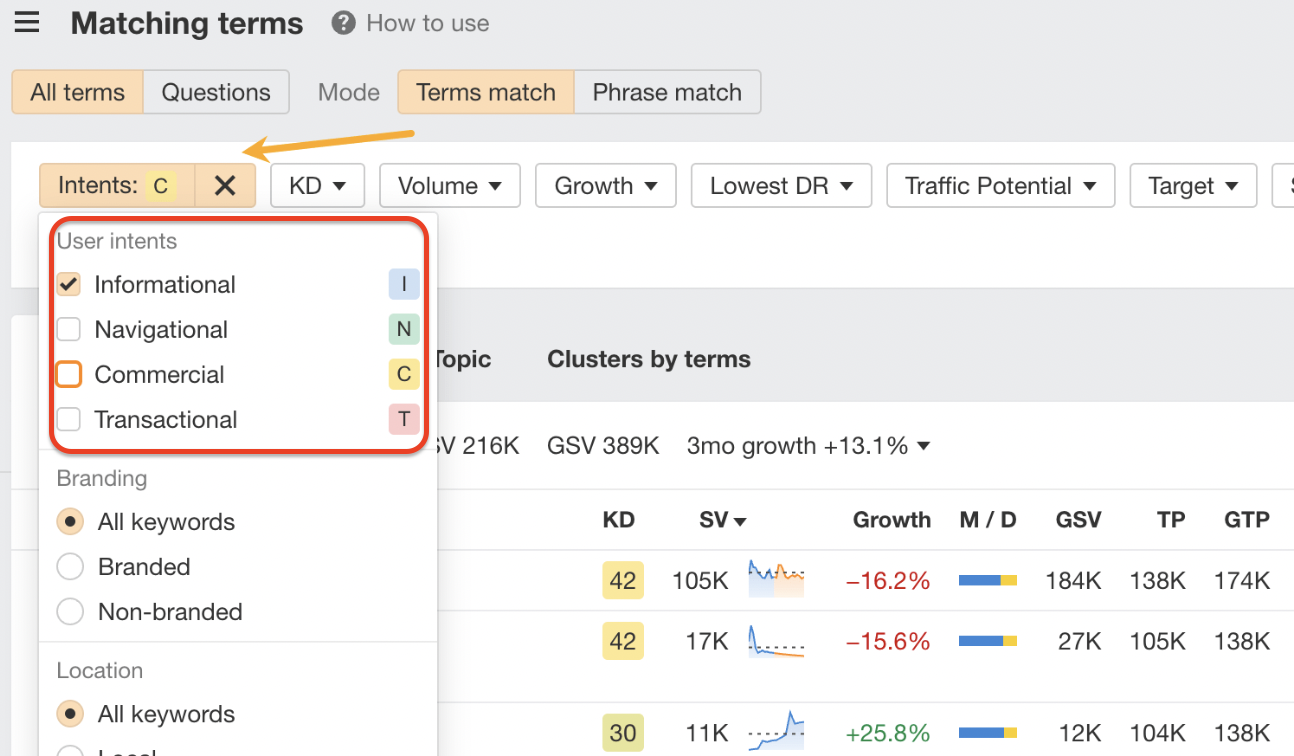
This is where most content hubs typically fall short. They create spoke pages without understanding why people search for each term.
- Informational intent: “What is content marketing?” (They want definitions and overviews)
- Commercial intent: “Best content marketing platforms” (They’re comparing options)
- Transactional intent: “HubSpot pricing” (They’re ready to buy)
Your hub page typically targets informational intent. Your spoke pages should match the specific intent of their target keywords. Don’t write a 3,000-word educational guide for someone who just wants a pricing comparison.
Step 4: Design Your Hub Architecture
Your hub page should:
- Provide a concise overview (not exhaustive—save depth for spokes)
- Link to every major spoke page with clear, descriptive anchor text
- Use a logical hierarchy (H2s for main subtopics, H3s for sub-sections)
- Include visual navigation aids (clickable content table, visual links)
Your spoke pages should:
- Satisfy search intent completely (the person should not need to click away)
- Link back to the hub page (reinforcing the relationship)
- Link laterally to related spokes when relevant
- Go deep on their specific topic (this is where you dive deeper)
Step 5: Build for Discovery
Even with perfect internal links, people need multiple ways to find content:
- Search functionality: Especially for content databases with 50+ pieces
- Filter options: By topic, format, audience, or publication date
- Visual hierarchy: Unique thumbnails, not generic stock photos
- Breadcrumb navigation: Shows the path from the hub to the current spoke
Step 6: Write Hub vs. Spoke Content Strategically
Hub page content principles:
- Broad overview that answers “What is this topic and why should I care?”
- Clear value proposition for why your hub is the definitive resource
- Strategic internal links naturally woven into the narrative (not just a list of links at the bottom)
- Approximately 1,500-2,500 words (comprehensive but not exhaustive)
Spoke page content principles:
- Deep, specific answers to one focused question or subtopic
- 1,000-3,000 words depending on complexity and search intent
- Multiple formats where appropriate (text, video, interactive tools)
- CTAs aligned with where the visitor is in their journey
Step 7: Master Internal Linking Architecture
This is the engine that makes everything work:
Hub-to-spoke links: Your hub page should link to every primary spoke, using descriptive anchor text that naturally includes target keywords. Avoid generic “click here” or “learn more.”
Spoke-to-hub links: Every spoke should link back to the hub (often in an intro paragraph like “This article is part of our comprehensive guide to [topic]”).
Lateral spoke links: When spoke pages naturally relate, a link is created between them. If your spoke on “content marketing for SaaS” mentions SEO, link to your “SEO for SaaS” spoke if it exists.
Equity flow: Your hub page naturally accumulates authority from external backlinks and should distribute that equity to spokes through internal links.
Step 8: Launch, Promote, and Actually Maintain It
SEO optimization checklist before launch:
- Descriptive, keyword-rich URLs with a hierarchical structure
- Schema markup (FAQ, Breadcrumb, ItemList, Article)
- Optimized title tags and meta descriptions
- Internal linking is fully connected
- Mobile-responsive design
- Fast page load times
Promotion strategy:
- Email your existing subscribers about the new resource
- Share hub and spoke content across social channels
- Build external backlinks to your hub page specifically
- Consider paid amplification for the hub page to jumpstart authority
Maintenance plan:
- Review bounce rates and time-on-page quarterly to identify weak content
- Update spokes as information changes (this is why evergreen content matters)
- Add new spokes as you identify content gaps
- Monitor keyword rankings and adjust based on performance
Content Hub SEO: Technical Essentials You Can’t Skip
URL Structure That Makes Sense
example.com/content-marketing/ ← Hub page
example.com/content-marketing/b2b-strategy/ ← Spoke page
example.com/content-marketing/b2b-strategy/linkedin-tactics/ ← Sub-spoke
Keep it shallow (2-3 levels maximum) and descriptive. Avoid complex process URLs with random numbers or dates.
Schema Markup That Helps Search Engines Understand
- Breadcrumb schema: Helps Google display navigation paths in search results
- ItemList schema: For your hub page’s list of spoke links
- Article schema: For individual spoke pages
- FAQ schema: If your content includes common questions and answers
What to Index (And What to Hide)
Index these:
- Hub pages
- Spoke pages
- Significant sub-spokes with unique content
Consider noindex for:
- Filter result pages in content databases (creates duplicate content issues)
- Tag archives that duplicate the hub organization
- Pagination pages beyond page 1
How to Actually Use Your Content Hub (Beyond Just Having It)
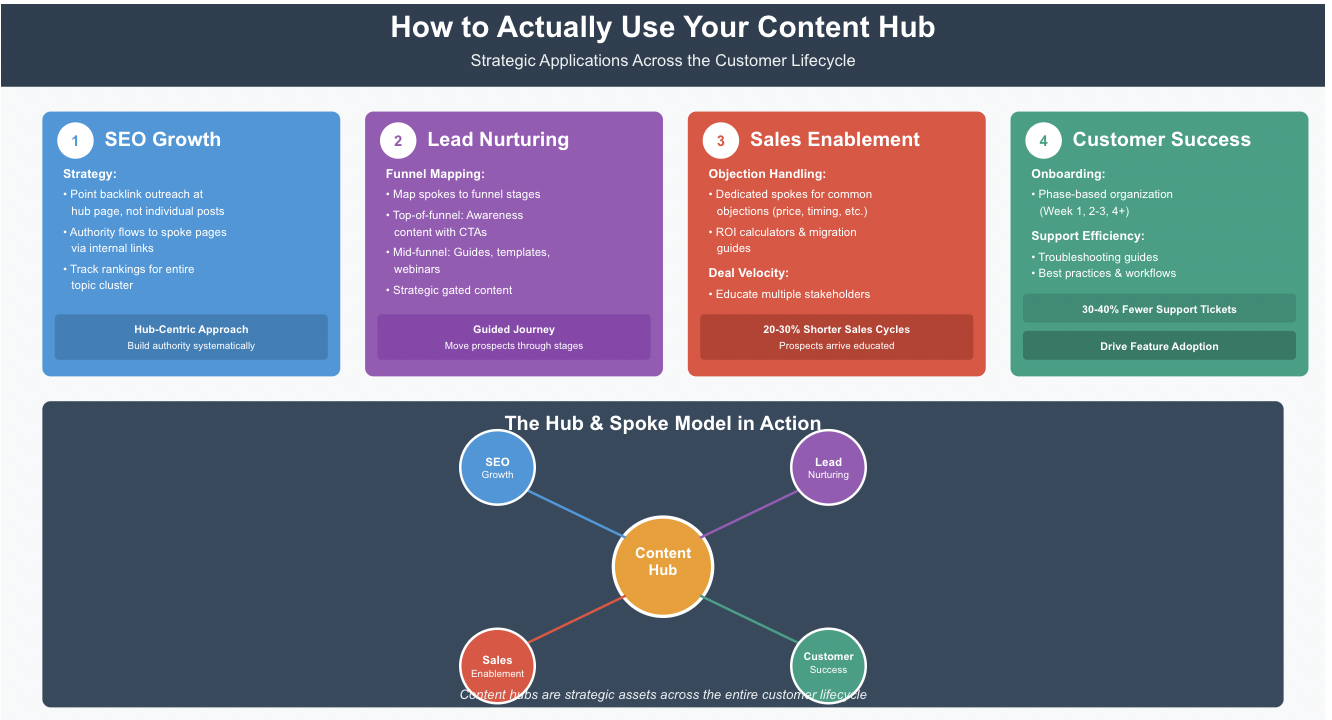
For SEO Growth
Point your backlink outreach at your hub page, not individual blog posts. When you earn a quality backlink to your hub, that authority flows throughout your spoke pages via internal links. Track rankings for your entire topic cluster, not just individual keywords.
For Lead Nurturing
Map content hub spokes to funnel stages. Top-of-funnel prospects read your awareness-level hub content and encounter CTAs for mid-funnel resources (guides, templates, webinars). Include gated content strategically within relevant spokes—not on every page.
For Sales Enablement
Your sales team can share relevant spoke pages directly with prospects based on their specific questions. No more sending blog archives—just: “Here’s our comprehensive resource on [their exact pain point].”
Beyond simple content sharing, content hubs become powerful sales tools when implemented strategically:
Objection Handling at Scale
Sales reps encounter the same objections repeatedly: “Too expensive,” “We already have a solution,” “Wrong timing,” or “Need executive buy-in.” Instead of crafting individual email responses, your content hub should include dedicated spoke pages addressing each common objection.
Example structure:
- Hub: “Choosing the Right [Your Category] Solution”
- Spoke 1: “ROI Calculator: When [Solution] Pays for Itself” (addresses price objections)
- Spoke 2: “Migration Guide: Switching from [Competitor]” (addresses status quo bias)
- Spoke 3: “Executive Briefing: Building the Business Case” (enables champion selling)
When a prospect raises an objection, your rep simply shares the relevant spoke page—which comprehensively addresses the concern with data, case studies, and clear next steps. This approach scales your best sales arguments across your entire team while keeping prospects engaged with owned content rather than losing them to competitor research.
Deal Velocity Through Education
Complex B2B sales often stall because stakeholders don’t understand the problem, solution, or implementation process. Content hub spokes can accelerate deals by:
- Educating multiple decision-makers simultaneously (share one hub link instead of booking separate calls)
- Providing due diligence materials (technical specs, security documentation, integration guides)
- Demonstrating implementation success (customer stories organized by company size, industry, or use case)
Sales teams using content hubs report 20-30% shorter sales cycles because prospects arrive at conversations already educated and aligned.
For Customer Success and Onboarding
Content hubs aren’t just for acquisition—they’re powerful retention tools when deployed post-sale:
Self-Service Onboarding Hubs
Instead of overwhelming new customers with generic welcome emails, create a dedicated onboarding hub organized by user role and implementation phase:
Phase-Based Organization:
- Week 1: Account Setup & Configuration
- Week 2-3: Core Feature Adoption
- Week 4+: Advanced Features & Optimization
Each phase includes relevant tutorial videos, documentation links, template downloads, and success metrics to track progress. Customers can move at their own pace while your CS team focuses on strategic check-ins rather than answering basic “how-to” questions.
Reducing Support Ticket Volume
When customers encounter issues, most immediately search your knowledge base or Google their question. A well-structured customer success hub with strong internal linking ensures they find answers within your ecosystem:
- Troubleshooting spokes organized by feature or error type
- “How-to” guides for common workflows
- Best practices from successful customers
- Integration documentation and API references
Companies with comprehensive customer success hubs report 30-40% reductions in support ticket volume, freeing CS teams to focus on expansion opportunities rather than reactive firefighting.
Driving Feature Adoption
Most SaaS customers use 20-30% of available features. Content hubs can systematically drive adoption:
- Feature spotlight spokes explaining business value and use cases
- Customer stories demonstrating ROI from specific features
- Step-by-step activation guides with video walkthroughs
Link these spokes in proactive email campaigns based on usage data: “We noticed you haven’t tried [Feature X] yet—here’s how it helped [Similar Customer] achieve [Specific Result].
Common Mistakes That Will Tank Your Content Hub
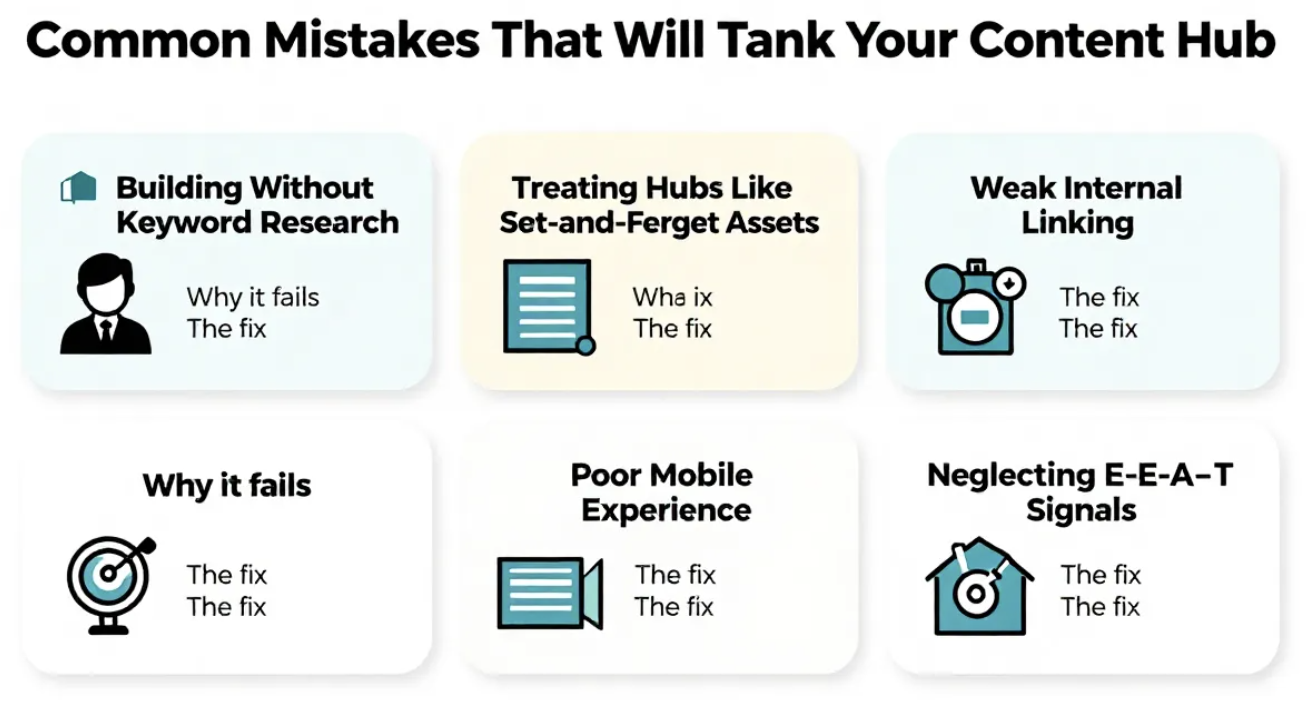
Building Without Keyword Research
The mistake: Creating a hub around topics you think matter without validating search demand.
Why it fails: Nobody searches for your made-up topic category. You’ve organized content beautifully around something nobody cares about.
The fix: Start with keyword research. Validate that people actively search for your hub topic and related subtopics.
Treating Hubs Like Set-and-Forget Assets
The mistake: Publishing your hub, promoting it once, then never touching it again.
Why it fails: Information decays. Your 2024 content becomes less relevant in 2026. Competitors publish fresher content. Your rankings decline.
The fix: Schedule quarterly content reviews. Update statistics, refresh examples, add new spokes as you identify gaps, and remove or consolidate underperforming content.
Weak Internal Linking
The mistake: Adding a bulleted list of related articles at the bottom of your hub page with generic “related posts” headings.
Why it fails: Search engines and users ignore generic link blocks. You’re not passing equity strategically, and you’re not creating a narrative journey.
The fix: Contextual internal links woven naturally into your content with descriptive anchor text. “To understand how content hubs improve SEO performance, read our guide to topic cluster strategy” is infinitely better than “Related: SEO Guide.”
Why it fails: Over 60% of searches happen on mobile devices. If your hub is desktop-optimized only, you’re losing the majority of potential visitors. Mobile users will immediately bounce if navigation is confusing, load times are slow, or text is unreadable without zooming.
The fix: Mobile-first design is non-negotiable in 2026. Test navigation, load times, and readability on actual phones, not just responsive design testing tools. Implement:
- Hamburger menus or collapsible navigation for hub sections
- Thumb-friendly tap targets (minimum 44×44 pixels)
- Lazy loading for images and videos to improve mobile load times
- Simplified spoke page layouts that prioritize content over sidebar widgets
- AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) or similar frameworks for content-heavy spokes
Google’s mobile-first indexing means your mobile experience IS your SEO performance. A hub that works poorly on mobile will never achieve its ranking potential, regardless of content quality.
Neglecting E-E-A-T Signals
The mistake: Publishing comprehensive content hubs without demonstrating Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—especially when using AI-generated content without proper human oversight.
Why it fails: Google’s algorithms increasingly prioritize content that demonstrates genuine expertise and real-world experience. In 2026, generic AI-generated content hubs lack the specific details, original insights, and credible authorship that search engines reward. This is particularly critical for YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) topics like health, finance, and legal advice.
The fix: Implement a mandatory “human-in-the-loop” editorial process:
- Author bylines with credentials and linked author bio pages
- Publication and last-updated dates clearly displayed
- Original research, case studies, or proprietary data that AI cannot replicate
- Expert quotes and interviews from named industry professionals
- Clear disclosure when content is AI-assisted, coupled with thorough human fact-checking
- Citations to authoritative sources (not just linking to yourself)
- Real customer testimonials, reviews, or user-generated content
If you’re using AI tools to draft content hub sections, treat them as first drafts requiring significant human refinement: add personal experience, update with current examples, inject brand voice, and verify every factual claim. The goal is AI-assisted content creation, not AI-generated content publication.
Google’s Search Quality Raters explicitly evaluate E-E-A-T signals. Content hubs lacking these signals—even if technically well-structured—will struggle to rank in competitive spaces.
Measuring Success: KPIs That Actually Matter
SEO Metrics to Track
- Keyword rankings: Track your hub page for head terms AND spoke pages for long-tail variations
- Organic traffic growth: Total visits to hub + all spokes combined
- Crawl stats: Are search engines discovering and indexing your content efficiently?
- Assisted conversions: How often does hub content appear in the conversion path?
Engagement Metrics That Reveal User Behavior
- Time on page: Hub pages should average 2-3+ minutes; low times suggest content isn’t engaging
- Pages per session: Good content hubs average 3-5+ pages per visit
- Scroll depth: Are people reading your comprehensive content or bouncing early?
- Return visitor rate: Great hubs bring people back repeatedly
Pipeline Metrics (For B2B Especially)
- Content downloads: How many gated assets are consumed from hub traffic?
- MQLs influenced: Track which leads engaged with hub content before converting
- CTA click-through rates: Are your strategically placed CTAs actually working?
- Attribution: Use multi-touch attribution to see hub content’s role in closed deals
The Honest Truth About Content Hub Costs
The Free Approach: Time + Your Current CMS
Actual investment: 40-80 hours of planning, content creation, and implementation for a 10-15 page hub.
What you can build: A fully functional hub-and-spoke structure with manual organization, strategic internal linking, and basic filtering/navigation.
Limitations: Requires ongoing manual maintenance. No advanced automation, personalization, or enterprise-scale asset management.
Best for: Businesses with fewer than 100 content pieces, small marketing teams, or anyone validating the content hub strategy before investing in software.
Mid-Tier Software: $500-$2,000/Month
What you get: Platforms like HubSpot Content Hub Professional—A/B testing, SEO recommendations, content analytics, lead capture tools, workflow automation.
When it makes sense: You publish 10+ content pieces monthly, have a team of 3-8 marketers, and lead generation is a primary goal.
ROI consideration: If your hub generates 50+ qualified leads per month worth $100 each, a $500/month tool pays for itself quickly.
Enterprise Solutions: $50,000-$250,000+/Year
What you get: Sitecore Content Hub, Adobe Experience Manager, or similar platforms with enterprise DAM, complex workflows, multi-site management, advanced brand guidelines enforcement, and API-first architecture.
When it makes sense: Managing 10,000+ digital assets, serving dozens of markets/brands, requiring enterprise-grade security and compliance.
ROI consideration: At this scale, efficiency gains from centralized content management and preventing brand inconsistency justify the investment.
The Future of Content Hubs: What’s Coming in 2026 and Beyond
Headless Architecture Is Winning
Traditional CMSs lock your content into one presentation layer (your website). Headless systems separate content from presentation, enabling omnichannel delivery through API-first architectures—your content hub becomes a central source of truth feeding multiple digital experience touchpoints.
API-First Content Delivery
The shift toward API-first platforms like Sitecore Content Hub ONE, Contentful, and Sanity allows content to flow seamlessly across channels:
- Mobile applications (native iOS/Android apps pulling content via REST or GraphQL APIs)
- Voice assistants (Alexa Skills and Google Actions pulling spoken content dynamically)
- IoT devices (smart displays, kiosks, in-store digital experiences)
- AR/VR experiences (spatial computing interfaces requiring structured content delivery)
- Future channels that don’t exist yet (your content structure remains portable)
Instead of “create once, publish to website,” the 2026 model is “structure once, publish everywhere.” Your content hub’s taxonomy, metadata, and relationships become portable assets that work across any interface.
The Technical Shift
Traditional monolithic CMSs:
- Content and presentation are tightly coupled
- Redesigning your website requires content migration
- Each new channel (mobile app, voice) requires rebuilding content structures
Headless/API-first systems:
- Content exists independently with structured metadata
- GraphQL or REST APIs allow any application to request exactly the content it needs
- Change your website design without touching content
- Launch new channels by simply connecting to existing content APIs
Real Implementation Example
A B2B SaaS company with a headless content hub architecture:
- Content team creates product documentation once in Contentful
- Website pulls formatted articles via API
- Mobile app displays the same content with app-optimized layouts
- AI chatbot uses the same content to answer customer questions conversationally
- Sales enablement app lets reps access content offline via API caching
When content updates, all channels reflect changes instantly—no republishing required across platforms.
When Headless Makes Sense
Consider API-first architecture if:
- You publish to 3+ distinct platforms (web, mobile, voice, etc.)
- Developer resources are available to build API integrations
- Content reuse across channels is a priority
- You need to future-proof against platform changes
For most SMBs publishing primarily to websites, traditional CMSs remain simpler and more cost-effective. Headless architecture solves distribution problems most businesses don’t yet have.
AI Is Changing Everything (But Not How You Think)
AI won’t write your content hub for you (and if it does, you’ll lack the authoritative expertise search engines reward). Instead, AI tools will:
- Identify content gaps by analyzing search trends and competitor coverage
- Automate tagging and taxonomy across thousands of assets
- Personalize hub navigation based on visitor behavior and intent
- Remix existing content into new formats (turning blog posts into social snippets, video scripts, or email sequences)
Critical reminder: Google’s algorithms increasingly favor content demonstrating genuine expertise and experience. AI-generated content hubs without human expertise will fail, especially in YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) topics. Successful 2026 content hubs use AI for efficiency (research, outlining, formatting) while maintaining human expertise for accuracy, originality, and credibility.
The E-E-A-T Arms Race
As AI content floods the internet, search engines will get more aggressive about identifying genuine authority. Your content hub needs:
- Clear author credentials (who wrote this and why should I trust them?)
- Updated publication dates showing you maintain content
- External validation (backlinks from respected sources)
- Real examples and case studies (not just generic advice)
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a content hub differ from a blog?
A content hub differs from a blog in its structure and scope. While a blog is generally a collection of related posts listed in chronological order, a content hub is more expansive and organized. It typically includes various types of content categorized around specific themes or topics, providing a broader and more integrated approach to information presentation. Content hubs are also more strategic in nature, designed to guide visitors through learning paths or conversion funnels.
What role do analytics play in managing a content hub?
Analytics are crucial for understanding user behavior, measuring engagement, and determining the effectiveness of content. They help identify what topics draw the most interest, where users spend most of their time, and which types of content lead to conversions. This data informs content strategy adjustments, helping to optimize the content hub for better performance and user satisfaction.
What types of content are most effective in a content hub?
The most effective types of content in a content hub vary depending on the audience and objectives but generally include a mix of evergreen articles, how-to guides, videos, infographics, and case studies. Interactive content such as quizzes, assessments, and tools can also significantly enhance engagement by providing value that static content cannot.
How can content hubs be integrated with other marketing efforts?
Content hubs should be integrated with broader marketing strategies through cross-promotion on social media, linking to relevant sales pages, and including calls-to-action that funnel visitors to other marketing channels such as newsletters, webinars, or product demonstrations. Using content from the hub in email marketing campaigns or digital ads can also extend the reach and effectiveness of other marketing initiatives. This integration helps create a cohesive user journey and amplifies the impact of each marketing effort.
Conclusion
Developing a content hub requires good planning, creation, and optimization. But with the right strategic approach meeting your content hubs to keyword research and technical SEO best practices, opportunities to establish thought leadership and drive organic traffic are significant.
For best results, continuously analyze metrics and refine your approach based on data. Staying tuned into trends and releasing fresh perspectives keeps readers engaged.
If developing or optimizing content strategies is not your core focus, partnering with experienced professionals can relieve the burden. Companies like Lead Advisors specialize in comprehensive content solutions, including content hub implementations, editorial calendar management, and full-funnel SEO.
Implement thorough auditing and analytics to enhance continually. The content hub becomes a small business’ most impactful SEO asset by developing supplementary materials linking pillar pages.