Rankings were once a dependable way to estimate the volume of traffic; however, the link between the two has broken down. It is quite possible that your #1 ranking is overshadowed by AI Overviews, featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, paid ads, and Reddit threads. The scope of visibility on the SERP has extended from traditional organic results to SERP features, AI search engines, and multi-platform discovery.
Through this manual, I am going to reveal nine such visibility levers that will make your website a presence on these surfaces, draw the potential customers who will convert, and gauge the effect beyond the average position.
TL;DR
SERP visibility refers to the different places where a website can appear, not only on search engine results pages but also on AI search engines and discovery platforms.
This manual includes nine different ways:
- redefining visibility metrics beyond position tracking,
- optimizing for conversion quality over vanity metrics,
- claiming multiple SERP features simultaneously,
- crafting high-CTR snippets,
- winning AI Overview citations,
- capturing emerging trends early,
- diversifying across non-Google platforms,
- building strong brand entities, and
- measuring holistically across SEO and paid channels.
Concentrate on those places that will bring you money, not simply more visitors.
Redefine SERP Visibility So Rankings Are Just One Signal
First of all, I would like to change your mental model from rankings to visibility and impact. Rankings only inform you about your position in the search engine results pages; however, SERP visibility indicates if someone is actually noticing you there.
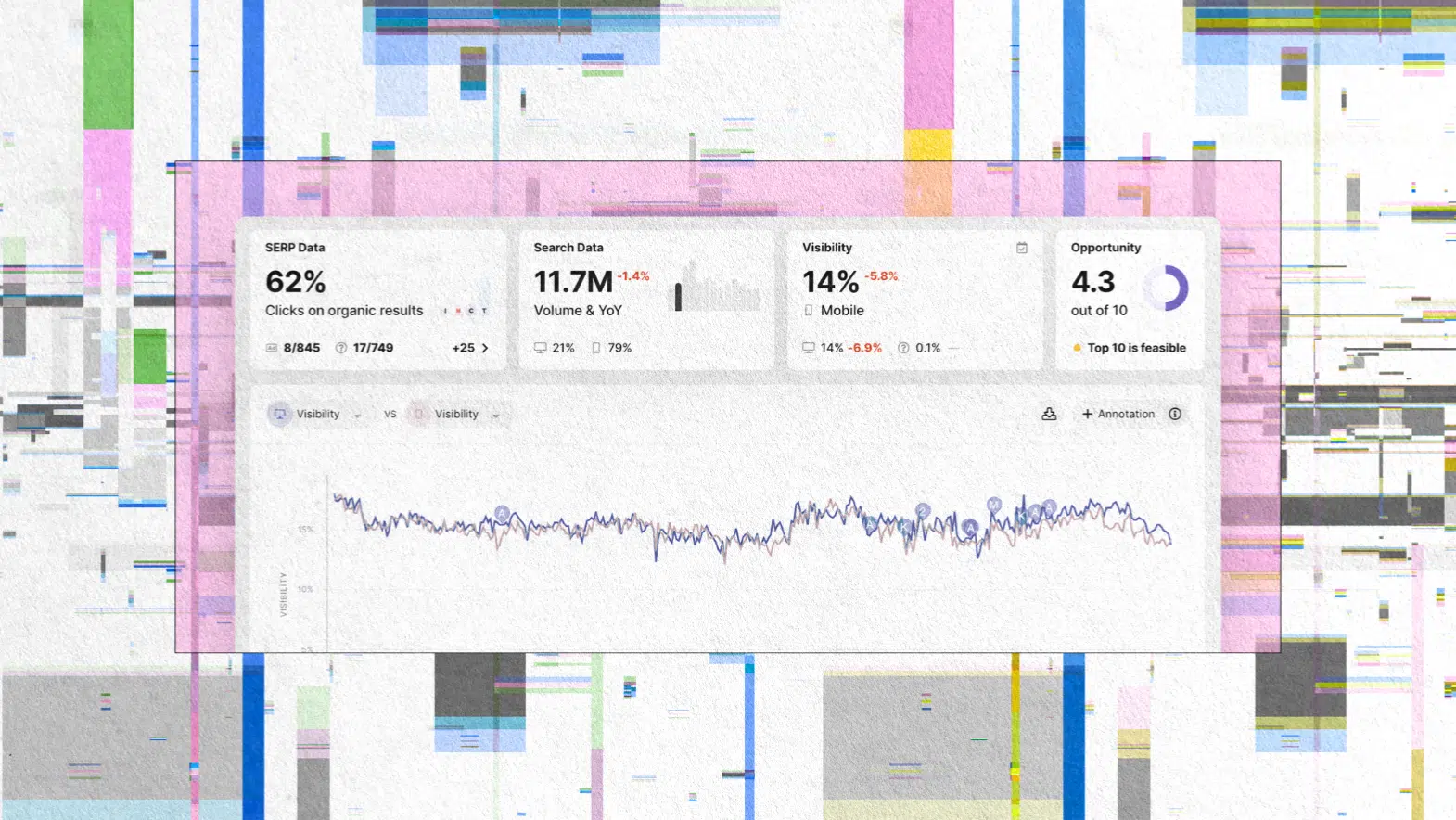
What Is SERP Visibility (and How Tools Calculate It)
SERP visibility definition is not just about simple position tracking. It is a measurable metric that indicates how prominently your brand is visible to the users of a search engine across the results for the tracked keywords. This visibility is influenced by the search volume and the expected click-through rate of the results.
Marketing Miner and other similar search engine optimization instruments determine visibility through this model: Visibility = search volume × CTR curve by position. The implication of this is that the fall from the first position to the third position affects the visibility considerably more than the shift from the fiftieth position to the fifty-third one.
Analysis of millions of Google search results reveals that the first position accounts for about 27.6% of the clicks, whereas the third position goes down to roughly 11% – thus, it is a 60% decrease in traffic for what appears to be a slight change.
SERP Feature Visibility vs. Classic Rank Tracking
Traditional keyword rankings are oblivious to the fact that SERP features are the main factor in the present search environment. It’s essential for you to be monitoring the percentage of visibility of the SERP feature – the percentage of the features available in the SERP that your site is taking for the relevant queries.
Think of a keyword such as “email marketing automation.” The Google SERP can show:
- AI Overviews with citations
- Featured snippets
- People Also Ask sections
- Knowledge panels
- Video results
- Image packs
- Standard organic listings
If the competitors are occupying five of these surfaces and you have only one blue link at position 2, then your real website visibility is very low despite the fact that you have a strong search ranking.
Why You Can “Rank” and Still Be Invisible
Same keyword, same ranking position but totally different visibility contexts. Just think about the third ranking for a high-value search term. You could be on a neat SERP without many features in one case, and get good organic traffic.
In the other case, the same position is beneath a four-paragraph AI Overview, a featured snippet of a competitor, an expanded People Also Ask section, a Reddit thread, and a video carousel. Your traffic potential in the second scenario may be only 3% of the first one.
That is the reason why getting better SERP visibility is a matter of optimizing for contexts and surfaces rather than just going up in positions.
Optimize for Visitor Quality, Not Vanity Impressions
High SERP visibility is of no use if visitors quickly leave the site or do not take the desired actions. According to a study conducted by Stanford, 75% of the users do not go beyond the first page of search results; however, getting a spot on the first page is of no use if it brings the wrong audience.
Visibility Only Counts If It Drives Action
I recommend tying SERP visibility to conversion-focused KPIs rather than vanity metrics:
| Business Type | Key Metrics to Track |
| B2B Companies | Demo requests, trial signups, marketing qualified leads, and closed-won revenue from organic search |
| Ecommerce Sites | Add-to-cart rates, purchase conversion rates, average order value, and customer lifetime value from organic traffic |
| Service Businesses | Contact form submissions, phone calls, appointment bookings, consultation requests |
The clearest insight of all: if your sessions are unchanged but your revenue per organic session goes up by 40%, it means that your search visibility has improved in the right place – among users who are searching with commercial intent and are the ones that actually buy.
How to Tie SERP Visibility to Revenue
The link between visibility and revenue is quite evident when you properly segment the performance. You need to configure tracking in Google Analytics in such a way that it distinguishes the performance of landing pages, intent classification, and SERP surface at the very least.
Landing page performance shows which pages are actually converting customers and which ones are just generating search traffic that bounces immediately. The reason why intent classification is important is that informational queries very rarely lead to immediate conversions, whereas commercial and transactional search terms should demonstrate significantly higher conversion rates.
Developing a simple monthly dashboard that links visibility metrics with business outcomes is a good idea. Keep track of visibility score by keyword theme, conversions generated, cost per acquisition, and revenue contribution. Such a model changes the somewhat vague SEO visibility enhancements into tangible business results that your management team is genuinely interested in.
Finding “High-Visibility, Low-Conversion” Problem Pages
Use Google Search Console together with your analytics to find immediate opportunities. This is what you should check out:
High impressions + Low CTR = Your snippet might not be attractive, or your page title may not be related to the search intent. These pages are losing the potential of their visibility.
High CTR + Low conversion rate = Your snippet is giving the wrong users the idea that your content is something different, so they are either setting the wrong expectations or misaligned ones.
Pages with 10,000+ monthly impressions but less than 2% CTR are a kind of low-hanging fruit. Even small changes to snippet quality can have a big effect because the visibility base is already there.
Own More SERP Real Estate on Blended, Multi-Feature Results
Let me reframe your goal from simply getting one blue link to grabbing as much of the prime real estate as possible for your main topics.
According to GetStat’s 2024 analysis, features account for 65% of SERP visibility, reducing organic share, while Sistrix studies note frequent appearances across millions of keywords without hitting 96.9%.
Why Blended SERPs Make Single Rankings Less Meaningful
Think about the things that show up when a person types the phrase “project management software for agencies” into a search engine.” The SERPs could have AI-generated answers, featured snippets with comparison tables, PAA sections, video results showing product demos, image packs, knowledge panels, and standard organic listings.
Intelligent companies try to be visible in three to four of these different places at the same time on the same page. A #1 position single is nearly obsolete when your competitors are present at the AI Overview, featured snippet, video carousel, and People Also Ask section for the identical query.
Mapping the SERP Layout for Your “Money Topics”
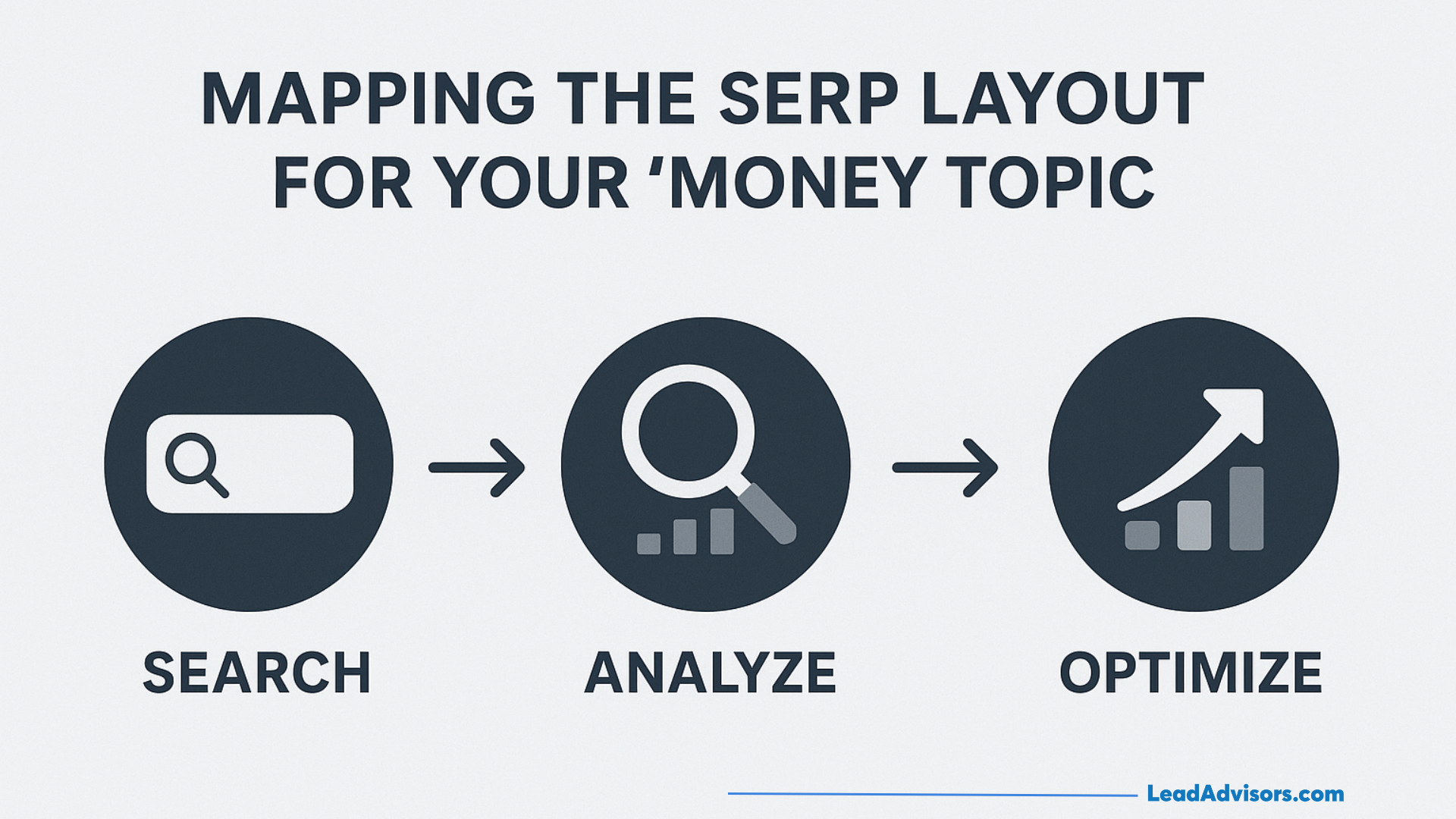
I suggest using the Search → Analyze → Optimize method to more effectively and in a structured way capture more SERP real estate:
- Search – Take a manual look at your top 50 revenue-generating keywords by typing them one by one in the search bar and note which SERP features are appearing consistently. Since this layout varies by device and location, you should perform the test from different contexts.
- Analyze – Determine the features that are present more than 70% of the time, the platforms that you are currently using, the places where your competitors are dominating, and which features correspond to high conversion rates according to your analytics data.
- Optimize – Decide your priorities based on the balance between the effort and the resulting impact. Usually, a featured snippet may require less effort than creating enough authority for knowledge panels; however, both can have a great effect on visibility.
Choosing Which Features to Chase for Each Intent
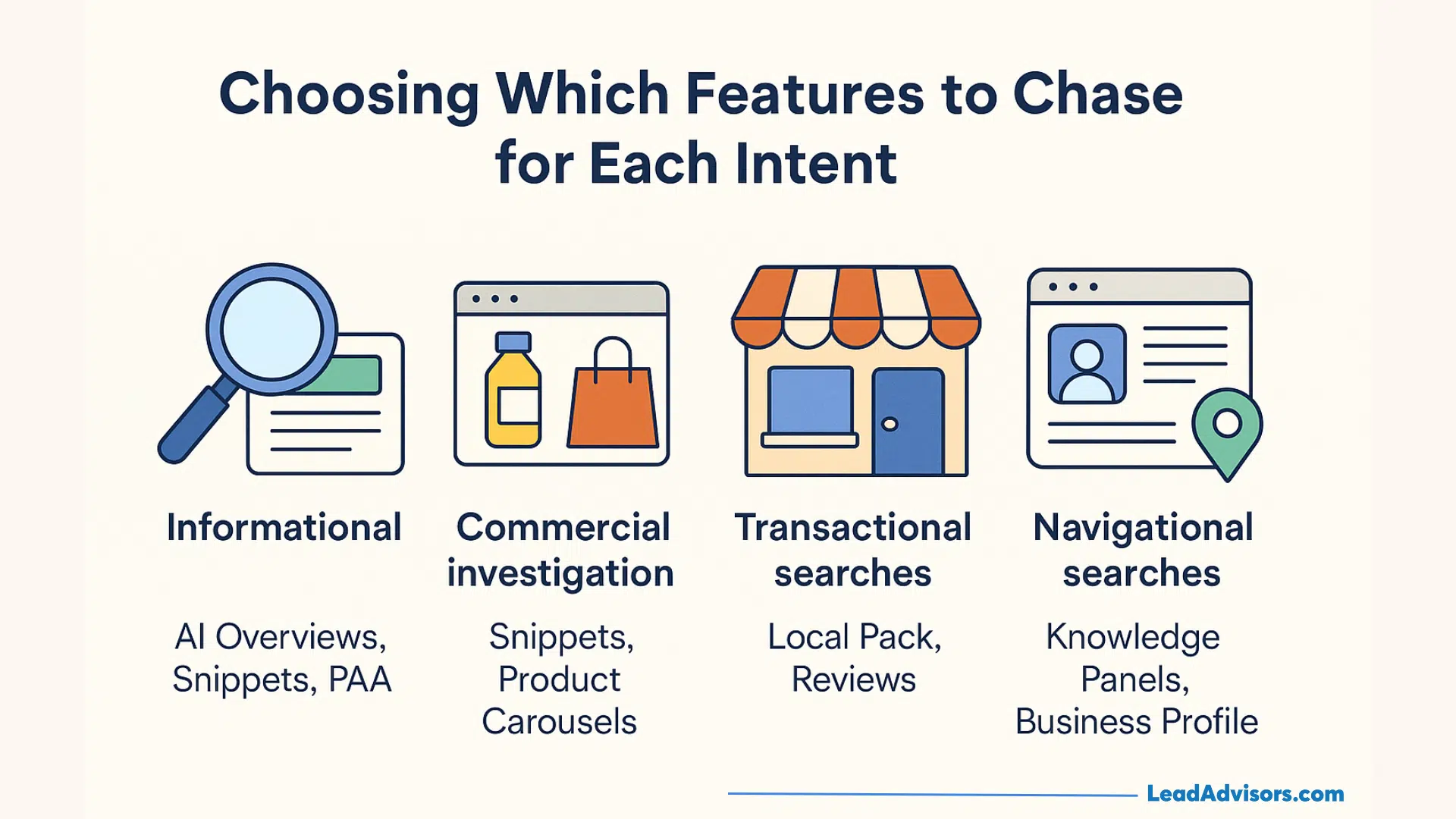
Match your optimization efforts to user intent rather than chasing every possible feature:
Informational queries → Mainly AI Overviews, featured snippets, and People Also Ask sections should be prioritized. Users want brief answers in easily scannable formats.
Commercial investigation → Aiming at featured snippets, product carousels, and rich snippets with ratings that show differentiation would be the best strategy.
Transactional searches → Emphasis should be placed on product carousels, local pack results for location-based businesses, rich site links, and prominent review ratings that help in building trust.
Navigational searches → It is advisable to support knowledge panels, enlarge site links, and enhance your Google Business Profile.
Design Titles and Snippets That Win the Click on Crowded SERPs
Being at the top of the page doesn’t necessarily mean that your content will be seen or clicked when there are AI Overviews, paid ads, featured snippets, Reddit threads, and video results all on top of your organic listing.
The meta title and description of your site are like small landing pages that have to convince the user to scroll further and to get the click.
Why Snippet UX Matters More in an AI-Heavy SERP
Backlinko gathered research from 5 million search results to figure out that emotional titles with power words raised the click-through rate by 13.9% in comparison to neutral phrasing. Such an effect is much stronger nowadays when the first page of a search engine contains a lot of different content formats, and users have to scroll several times before they come across your listing.
Make sure that your titles and descriptions are formatted correctly for all the different devices by using snippet preview tools before you publish. Google shortens titles based on the number of pixels and not characters; thus, the same 60-character title might be fully displayed or get shortened depending on which letters are used.
Pixel-Safe Titles and Descriptions in Practice
Here’s what I recommend for crafting snippets that convert:
Title Tags
Don’t think of them as just a bunch of keywords, but rather as the copy for your ads. Use your main keyword along with the result that the user is searching for will want in the first part of the sentence, keep it under about 580 pixels (around 50-60 characters), and put your brand only if it is helping to gain the user’s confidence. For example, you can write a title like “Best CRM Software 2025” and add the year in it to let users know that your content is up-to-date.
Meta Descriptions
Advertising is simply showing off the goods or service with the benefit front and center, a credibility marker, and a very soft call to action. The very first 120 characters should contain the most important information, as the mobile preview is shorter. Be aware that Google sometimes adds dates dynamically which take up your valuable space.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Having the same generic templated descriptions for hundreds of pages diminishes the chances of your CTR. Users get annoyed with keyword stuffing that makes the text less readable. Not paying attention to mobile optimization is a mistake of the highest order when more than 60% of the searches are done on mobile devices.
Where to Prioritize Snippet Tests in Your Portfolio
It is not necessary to spend the same amount of time on each page. Pages with a stable ranking but a weak click-through rate should be the ones you look at first. In other words, pages that are at positions 3-7 and have a CTR below average are the ones that can bring you the most quick wins. Just a 20% increase in the CTR in such a place could lead to a considerable flow of new visitors without you having to make any changes to your search rankings.
Moreover, focus on the pages that have a high commercial potential and a large volume of traffic, like product category pages and service offerings. In case these pages have a great search volume, but the number of conversions is low, it could mean that the snippets are not properly aligned and therefore, the expectations of users are incorrect.
Optimize for AI Overviews and LLMs, Not Just Classic SERPs
SEO is a method to optimize pages so they can rank high in search engines and get more clicks. GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) is more about making your brand become the go-to one for citation and mention in AI-generated answers. Although these two strategies are somewhat related, they differ in terms of their goals and the way they achieve them.
SEO vs GEO: Different Goals, Overlapping Tactics
A study revealed that large language models (LLMs) use references from the top Google search results in more than 89% of cases. However, merely being listed in the conventional search results does not ensure that your content will be part of AI summaries or ChatGPT answers.
Firstly, you have to comprehend the three different types of AI-powered search systems:
| System Type | Examples | How They Work | Optimization Focus |
| Training-based | GPT-4 (offline) | Trained on data with a cutoff date | Build authority, get cited by high-authority sites before training windows |
| Real-time search | AI Overviews, Perplexity, Bing Chat | Pull live results when generating responses | Structure content for fast retrieval and clean parsing |
| Hybrid | ChatGPT with browsing, Gemini | Combine training knowledge with real-time fetching | Both authority building and technical optimization |
How AI Overviews Choose Who to Cite
Neither Google nor AI search engines disclose their exact algorithms. However, by analyzing thousands of queries, one can find certain patterns. AI systems want a single page to cover the topic in detail, thus answering not only the main question but also several related questions.
They also value a clear structure with the headings being not only descriptive but also very close to the way the question would be formulated if asked in a natural language. The use of a conversational style, which is similar to the way people actually ask questions, and the inclusion of concrete examples instead of vague generalizations are also some of the factors that AI systems take into consideration.
If the content is loading slowly, requires complex JavaScript rendering, or is behind a paywall, then it will not be considered. AI crawlers have a shorter timeout than a regular Googlebot; hence, site speed and a site with a clean layout are very important.
Simple GEO Wins You Can Implement Without New Headcount
Start with these high-leverage, low-effort tactics:
- Add FAQ schema with structured data using Schema.org FAQPage markup on pages answering common questions
- Create comparison content since AI search platforms heavily favor “X vs Y” and “Best tools for Z” queries
- Cite reputable sources by linking to .edu, .gov, and established industry authorities to signal credibility
- Build entity associations by getting mentioned in industry publications and review platforms
- Optimize page speed targeting Core Web Vitals, especially for mobile optimization
Read more: LLMO vs. GEO vs. AEO: How to Win Mentions, Citations, and Conversions from AI
Use Trendspotting to Capture Visibility While Competition Is Low
Low-volume, rising topics represent visibility gold. I’ve seen early movers on emerging trends capture both traditional search rankings and prime positioning in AI Overviews before competitors flood the space.
Where to Find Your Next High-Leverage Topic
Trend signals come from external discovery platforms and internal intelligence:
External Sources:
- Exploding Topics (tracks search volume growth across millions of terms)
- Google Trends (identifies rising queries and regional interest spikes)
- Social listening across Reddit and industry forums
- Industry publications and conference topics
Internal Intelligence:
- Google Search Console’s “new queries” report
- Sudden impression surges on existing content
- Site search data showing what visitors look for but can’t find
- Customer support tickets and sales team questions
Stanford research on information diffusion found that content published during the early adoption phase of trending topics receives 7.2 times more sustained engagement than content published after mainstream adoption.
A Simple Sprint Workflow for Trend-Led Content

Most teams overcomplicate trend response. I recommend this lightweight monthly sprint:
Week 1 – Take an inventory of all trend data sources, look through them, and shortlist 5-10 emerging topics that are relevant to your audience, check that each has some existing search volume (even 100-500 monthly searches), and see the current SERP competition.
Week 2 – For each topic, prioritize the score on product alignment (1-5), growth (1-5), ranking difficulty (1-5, lower is better), and business impact potential (1-5). Instead of spreading resources thin, choose your top 1-2 topics.
Week 3 – Develop a detailed yet focused 1,500-2,500-word content explaining the trend, why it is important, and the practical applications.
Week 4 – Promote & Monitor through your owned channels, pitch to industry publications for backlinks, and track ranking movement on a weekly basis.
How to Keep Trend Content Updated Without Burning Your Team Out
The main error that I commonly come across is the act of publishing a work and then not following up with it. Have a look at your trend pieces every quarter, and for each update, just 30 minutes of spare time would suffice to do the following:
- Add the latest statistics
- Include recent examples
- Update the publish date
- Refresh at least one major section
If a trend goes down, redirect to the related content. If a trend goes up, broaden it to a full content cluster. Such a small-maintenance operation of your content keeps it at the level of the market without the need for complete rewrites every month.
Grow Visibility Across AI, Social Search, Marketplaces, and UGC
If 80-90% of your discovery traffic flows through Google search results alone, your brand faces critical vulnerability. Algorithm updates or AI Overview expansion can crater organic traffic overnight.
Why Google-Only Visibility Is a Business Risk
Gen Z heavily favors social platforms: 77% use TikTok for product discovery (the highest among platforms), and 61% turn to Instagram for purchases. Among 18-24-year-olds, 67% use Instagram and 62% TikTok to find local businesses, surpassing Google in some cases. Additionally, 71% of TikTok users discover new products there, with 33% making purchases post-exposure.
AI Search Engines – ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Bing Copilot, where the interaction is in the form of asking questions conversationally
Social Discovery Platforms – TikTok for product recommendations, Instagram for visual discovery, YouTube for tutorials, LinkedIn for B2B thought leadership
UGC Ecosystems – Reddit, Quora, niche forums that heavily influence the decision to purchase (Google now prominently features Reddit threads)
Review Platforms – Google Business Profile, G2, Capterra, Trustpilot, Yelp, Amazon, where buyers assess their options
How to Pick Your Top 2-3 Non-Google Surfaces
Don’t be tempted to optimize for each platform at the same time. This is how I strategically work:
- Find out where your potential customers are hanging out by doing customer surveys or looking at referral traffic in Google Analytics
- Do a competitive gap analysis to discover where your competitors are strong and where you are weak
- Evaluate platforms by the number of people that make up the audience, the potential for organic reach, the content production requirements, and the team’s capabilities
- Keep your focus very tight with only 2-3 platforms at most for the first quarter
Develop a consistent presence and understand what content works before getting bigger.
Tracking Non-Google Discovery Without Getting Lost in Data
Create a simplified monthly dashboard:
| Platform Type | What to Track | Success Indicator |
| AI Search | Citations, mentions, referral traffic | Increasing mentions quarter-over-quarter |
| Social Platforms | Reach, engagement, profile visits | Growing audience and engagement rates |
| UGC/Forums | Brand mentions, sentiment | Positive sentiment trending upward |
| Review Sites | Rating, review volume, velocity | Above 4.5 stars, steady review flow |
| Combined | Non-Google traffic %, conversions | 30%+ of total discovery traffic |
The key insight: you don’t need perfect attribution. Focus on whether your search presence is diversifying and whether revenue from non-Google sources trends upward quarter over quarter.
Turn Your Brand Into an Entity That Dominates Branded and Comparison Searches
Google and AI models don’t just index pages—they map entities, including brands, people, products, and concepts, along with relationships between them. Strong entity signals create compounding visibility advantages.
The Link Between Brands, Entities, and SERP Visibility
Consider entity-first SEO as the process of creating your brand’s “knowledge graph footprint.” The more you have these signals spread out over the internet, the more your content is getting visible by the search engines for the different relevant queries, even if you are not the page with the highest ranking.
Strong entity signals get you:
- Knowledge panels for your brand in Google SERP
- Brand bias in AI Overviews (AI systems favor mentioning recognized brands)
- Higher trust signals boost click-through rate on regular snippets
- Increased branded search volume from users who discovered you elsewhere
Some of the signals that help to strengthen your entity are branded search volume and brand-plus-modifier queries such as “[brand] reviews” and “[brand] vs [competitor].”
Having the entity data consistent on your website, structured data markup, Google Business Profile, LinkedIn, and major online directories will allow the search engines to understand your brand with confidence.
A Quick Audit of Your Entity and Review Footprint
Run this 30-minute assessment:
Branded Search Analysis
Look for the phrase “[your brand] review” and record the results that come up. In addition to that, find out the differences between your brand and the top three competitors by searching “[your brand] vs [competitor]” for each of them.
After that, search for “[your brand] pricing” and “[your brand] alternatives.” Note down the different SERP features that show up and mention if you have control over them.
Entity Consistency Check
Ensure that your name, address, phone number, and basic details are identical not only on your site (with Schema.org Organization markup) but also on Google Business Profile, LinkedIn, top directories, and industry databases. Discrepancies mislead search engines and weaken your entity signals.
Review Footprint Assessment
Perform an audit of your presence on the review platforms that are most relevant to you. Monitor your review volume (total reviews), rating (average stars), and recency (reviews in the past 90 days). New reviews indicate brands that are active and can be trusted.
How to Bake EEAT Into Your Content

Google’s E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) framework has a significant influence on your ranking level and whether AI systems refer to you:
Experience → Show that you understand the matter directly through new research and examples from the real world. In addition, the author should provide credentials and give detailed examples rather than making general statements.
Expertise → Have experts in the field evaluate the content and do not provide superficial advice, but rather give specific, actionable insights.
Authoritativeness → Get mentions and links from well-known industry/media sources. Become a panelist in conferences and publish your articles as a guest on websites with high authority.
Trustworthiness → Provide easy-to-find contact details, show security badges, give credit to trustworthy sources, and be open about your limitations.
User-focused content that actually helps users looking for solutions will, in fact, be these elements without any kind of forced credibility claims.
Measure SERP Visibility as One Portfolio Across SEO, AI, and Ads
Executive teams don’t care which team gets credit for conversions. They care about total search presence efficiency—does our investment drive profitable growth?
The KPIs That Actually Define SERP Visibility Today
Develop your measurement system using these core metrics as a foundation:
- SERP visibility score – A visibility measure that takes into account the weighted average of the tracked relevant keywords
- SERP feature visibility % – The percentage of the features available that you occupy for the most important themes
- AI visibility metrics – Citation frequency, share of voice vs. competitors
- Blended search conversions – The thematic performance resulting from the combination of organic and paid activities
- Visibility trends – The traffic diversification over different surfaces
Keep a record of total conversions (organic + paid) for each keyword theme, blended cost per acquisition, revenue contribution by theme, and conversion rate by search intent category. Identify the surfaces where the highest-quality potential customers are coming from, as indicated by the lowest CAC and highest lifetime value.
Sample Dashboard Layout Your C-Suite Will Understand
Create a one-page executive summary updated monthly with four sections:
Overall Search Impact
- Total search-driven revenue (month and YTD)
- Search’s percentage of total company revenue
- Blended search CAC vs. target
- Month-over-month growth rate
Visibility Scorecard by Theme: For each of your top 5-8 revenue-driving themes, it shows the combined visibility score with change, SERP features occupied (e.g., “3 of 7 – PAA, Featured Snippet, Video”), AI citations this month, organic + paid conversions with trend, and blended CAC with trend.
Diversification Health: Display traffic percentages: Google 72% (target <70%), AI search 8% (target 15%+), social search 11%, UGC/reviews 6%, other 3%.
Critical Actions: Provide 3-4 bullets on what’s working, what needs attention, and next month’s priorities.
How Often to Review and Iterate on Your Visibility Strategy

I recommend establishing this rhythm:
Daily (automated alerts) → Drastic ranking drops, site speed issues, big SERP layout changes
Weekly (15-30 minutes) → Google Search Console performance report highlights, traffic anomalies, competitor SERP movements
Monthly (2-3 hours) → Holistic KPI dashboard review, visibility trends analysis, Content performance prioritization, Emerging topic identification
Quarterly (half-day) → Review of search landscape shifts, assessment of diversification progress, major content calendar decisions, competitive intelligence deep dives
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I update content to maintain SERP visibility?
What is FAQ schema and should I use it?
Can I rank for multiple SERP features with the same page?
What are the biggest mistakes that hurt SERP visibility?
How do online directories and citations affect SERP visibility?
Conclusion
Nowadays, SERP visibility refers to the place where you are visible, how often, on what surfaces, for which relevant queries, and most importantly, what business results that visibility generates. In 2025, simply having good rankings will not be enough to secure a budget or get the executives on your side.
The nine strategies outlined in this manual serve as a comprehensive framework—regard measurement as something different from mere rank tracking, link visibility to conversion quality and revenue, be present in several SERP features for a single high-value query, create snippets that attract clicks, enhance your site for AI Overviews, identify topics that will soon be popular before your competitors, get your name known not only through AI and social platforms but also through traditional channels, strengthen brand entity signals, and have a holistic approach when you measure SEO, AI, and paid search.
I would suggest that you first conduct a truthful audit of your current visibility footprint. Go beyond looking at keyword rankings and see which SERP features you have control over against those your competitors have, how frequently AI systems refer to your brand, what proportion of discovery is coming from non-Google surfaces, and if your visibility is leading to high-quality organic traffic that converts. The terrain will keep changing, but the brands that choose to leverage multi-surface visibility today will be the ones to dominate tomorrow’s search results.