If you’re new to Search Engine Optimization (SEO), managing links might not be the first thing that comes to mind. But here’s the thing — your link structure actually plays a much bigger role in getting your content to rank.
Remember that bad links don’t just break pages, they break your SEO too. If the page can’t be found, so does the content. Small issues like these can lead to big problems and the last thing you want for your pages is dropped rankings, skipped pages, and a poor overall experience.
So what do you do? Well, let’s start off by knowing these two important link types: absolute and relative links. Both can help you out with your SEO, but depending on which one you choose affects how your pages are crawled, indexed, and ranked.
However, figuring out which one is better between absolute vs relative links has been a long-running debate among SEO experts. In this article, we’ll break down what each one does, when to use them, and help you make the right choice.
What Are Absolute and Relative Links?
Before we compare them, let’s understand what they are and how they work. These links are referred to as hyperlinks. They link one page with another, allowing search engines to understand the structure of your website.
Think of it this way. Your website is like a house, and each web page is a room. Hyperlinks are the doors between those rooms. If the doors are clearly labeled and lead to the right place, then finding your way around would be easy. But if there are no signs or some doors are missing, you’re more than likely to get lost, and the same thing happens when search engines try to crawl your site.
Now, there are two main types of hyperlinks:
- Absolute links – These are full URLs that include the protocol (like https://) and the site address.
- Relative links – These are shorter URLs that connect to a page based on its location within your site’s directory structure without including the full domain.
While they may look similar in your HTML code, using the wrong type in the wrong context can lead to SEO problems, broken links, or errors during site migrations.
So, when should you use one over the other?
What is an Absolute URL?
Think of it like a courier delivering a package, they won’t get lost as long as they have the full address. The same goes for absolute URLs, which provide the full path, making it easier for search engines to reach the correct destination. Here are some examples of how absolute URLs are used in different CMS platforms.
Content Management System | Description | URL |
WordPress | When you add a link or insert an image, WordPress usually generates an absolute URL by default. | <a href=”https://yourdomain.com /blog/post-title”>Read more</a> |
Shopify | Here, Shopify uses absolute URLs in structured data and canonical tags. | <link rel=”canonical” href= “https://yourstore.myshopify.com /products/product-name”> |
Wix | Wix automatically handles linking and typically uses absolute URLs for SEO elements like sitemaps and meta tags. | <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://yourwixsite.com/services”> |
Sounds simple enough, right? But to really take advantage of full domain paths, it helps to understand why absolute links are often the better choice for SEO and long-term site stability:
1. They Help Protect Against Content Scraping
We’re all aware of content theft, especially when AI does most of the dirty work through scraper programs. If your content is copied and republished on another site, absolute URLs will still point back to your original domain. Absolute links are excellent in terms of site security, as they maintain your SEO authority and reduce the risk of search engines indexing duplicate versions on someone else’s site.
2. They Reduce Duplicate Content Issues
Afraid of having multiple links lead to the wrong page? A small change to the URL, like http or https, www or without the www, Google treats each one as a separate page. That means your site might accidentally have four versions of the same content cannibalizing each other, such as:
- http://example.com
- https://example.com
- http://www.example.com
- https://www.example.com
To Google, these are four pages, not just one. Using an absolute path for your internal links helps avoid this issue by always pointing to the correct version. This keeps your site organized and helps search engines index pages accurately, especially across different https versions.
3. They Help Google Crawl Your Site Better
Google gives every site a crawl budget, which is a limit on how many pages it’s willing to crawl in a given timeframe. The more efficient your website structure, the better that budget is used. That’s where absolute links can help you make the most out of it. They create clear, direct routes across your site, making it easier for Google to crawl important information quickly and skip noise. It’s a simple change that can lead to better indexing and faster updates in search results.
What is a Relative URL?
Now that we’ve learned about absolute links let’s take a look at how relative links work. Every long route has a shortcut, and that’s what a relative URL is. Instead of using the full web address, a relative link connects to another page based on where you already are on the site. It skips the domain and protocol, which makes it shorter, easier to work with, and ideal for linking between pages on the same site. Here are some examples of how absolute URLs are used in different CMS platforms.
Content Management System | Description | URL |
WordPress | WordPress can use relative URL links, especially if you manually insert them or configure your theme or plugin that way. However, it usually defaults to absolute links unless changed. | <a href=”/about-us”>About Us</a> |
Shopify | In Shopify, relative paths are commonly used for internal navigation. | <a href=”/collections/all”>Shop Products</a> |
Wix | Wix mostly handles linking automatically and favors absolute URLs. However, relative paths may appear in code or preview environments during editing. | <a href=”/services”>Our Services</a> |
These links work around within the current site directory without needing a full web address. They’re mostly used for internal linking and are a simple and efficient way to connect pages without repeating the entire address. So, if you’re a web developer, they can come in very handy when working in development or on staging versions of your site.
Here’s why the relative format is often the better choice for internal navigation:
1. Cleaner, Shorter Code
Relative links keep your HTML tidy and easier to manage, especially when working with a lot of content.
2. Better for Staging and Development
Because relative links are tied to the current file structure, they adapt easily when testing on different environments like staging servers or local builds. You won’t have to manually update links when moving between versions of the same website.
3. Slightly Faster Load Times
The speed difference is small, but relative links can load a bit faster since the browser only needs to follow the path, not look up the full domain.
Do relative URLs really make your site load faster?
Some sources suggest that relative URLs slightly reduce load times because they avoid additional DNS lookups or SSL handshakes when referencing resources within the same domain. However, this difference is so small that it is unlikely to have a noticeable impact on user experience or SEO performance.
SEO Impact of Absolute URL Link vs. Relative: What Google Recommends

Whichever you’re using, that choice directly affects how Google crawls your site, indexes your pages, and passes ranking signals. It also impacts how your content holds up during site changes, migrations, or even when targeting different languages.
Let’s break it down.
Google’s stance: Does Google prefer absolute or relative URLs?
Technically, Google can handle both absolute and relative links. But if you pay attention to their best practice recommendations, it’s pretty clear they lean toward absolute URLs. Look at how most CMS platforms are set up, especially for things like sitemaps and structured data — they almost always default to absolute links. They give Google the full path with no guesswork involved.
So, if you’re planning out your SEO content strategy, sticking with absolute links is a smart move. It keeps things clean, consistent, and easy for search engines to crawl without confusion.
Duplicate content issues: How relative URLs can cause canonicalization errors
This is where things can get tricky. Relative URLs rely on the context of the page they’re on. If something like a <base href> tag is misconfigured, your relative link might point somewhere completely different. That can lead to duplicate versions of the same content getting indexed, and Google doesn’t always know which one to rank. Using absolute links helps avoid this by giving Google the exact path every time.
Dig Deep: Content Pruning: Get Rid of Your Website’s Dead Weight
Crawl budget considerations: How Googlebot treats absolute vs relative links.
Every site has a crawl budget a limit on how many pages Googlebot will scan during a visit to the entire website. If your links are inconsistent or point to duplicate pages, that budget gets wasted.Relative URLs also give a sense of duplicate content risk. absolute URLs provide security and help keep things clean. They give Googlebot a direct line to the content you want indexed. No detours, no wasted crawls.
Hreflang implementation: Which link type is best for multilingual SEO
If your site targets users in multiple languages or regions, you’ve probably worked with hreflang tags. In this case, absolute URLs are a must. Google’s documentation specifically recommends them because they remove any ambiguity about which version of a page is intended for which audience. It’s a small step that makes international SEO a lot more stable.
AI and search: How Google’s AI Overviews process absolute vs relative URLs
With AI-driven features like Google’s AI Overviews becoming more common, the structure of your site matters even more. These systems pull quick summaries and answers from web pages, and if your content is scattered or your links are inconsistent, it’s harder for AI to pull the right context. Absolute links make it easier for AI systems to trace the original source and interpret your content accurately.
Internal linking impact: The role of absolute vs relative links in distributing link equity
Internal links help distribute ranking power across your site — and both absolute and relative links can technically do the job. But here’s the catch: relative links are more fragile. If your site goes through a redesign, migration, or major restructure, those relative links can break or point to the wrong place. Absolute links hold up better. They make sure your internal linking stays consistent, and your link equity keeps flowing to the pages that matter.
Site Version Control: First Step Before Choosing Link Types
Before you even decide whether to use absolute or relative links, there’s one thing you need to lock in first — your site version. If your site is accessible in more than one way — like http://, https://, with or without www — search engines may treat each version as a separate site. That’s a big problem for SEO.
Why This Matters for SEO
Search engines want one clear version of each page. When they see duplicates, they’re not always sure which one to rank. That can hurt your visibility, weaken internal linking signals, and slow down indexing. If your links point to different versions of the same URL, you’re only making things harder for crawlers — and yourself.
Best Practices to Fix It
To keep your site clean and SEO-friendly:
- Set up 301 redirects to send all traffic to one preferred version — usually https:// and non-www.
- Use self-referencing canonical tags on every page to signal the correct version to search engines.
- Set your preferred domain in Google Search Console and check that your indexing settings are aligned.
Read More: How to Optimize a Website: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Protect SEO During Site Migrations

Site migrations, HTTPS upgrades, or moving from a staging domain to a live one can easily break internal links if you’re not careful. Here’s how to keep your SEO intact during the process:
1. Crawl Your Website
Before making any changes, run a full crawl with a tool like Screaming Frog. This gives you a full view of your site structure, links, and URL paths.
2. Update Internal Links
If you’re using absolute URLs, update them to reflect your new production domain. If you’re using relative URLs, make sure all paths still point to the right place after the move.
3. Set Up Redirects
Create a clear redirect map from your old URLs to your new ones. Avoid redirect chains — they slow things down and dilute SEO signals.
4. Test in a Staging Environment
Before going live, test everything in a staging environment. Make sure there are no broken absolute and relative URLs, no test domain references, and everything points to the correct live version.
5. Monitor After Launch
Once your new site is live, resubmit your sitemap in Google Search Console and monitor your crawl stats. Run another crawl to catch any last-minute issues and make sure everything is working as it should.
Tools to Audit and Manage Links
Even with a solid internal linking strategy, things can go wrong — links break, pages move, and updates slip through. That’s why SEOs use a few key tools to keep everything working as it should. These SEO tools help you spot issues early, fix them fast, and make sure your site stays easy to crawl and navigate.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
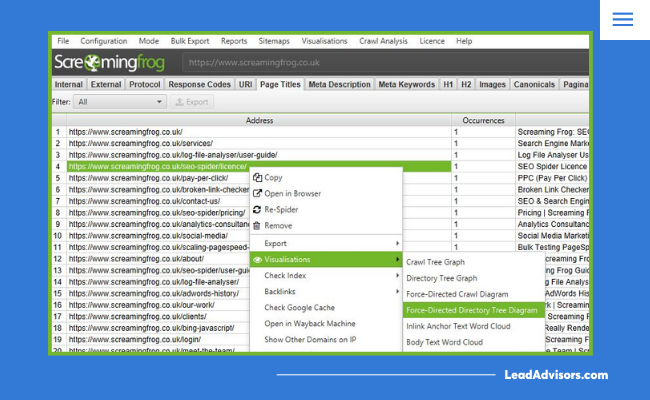
This tool crawls your site like Googlebot. It quickly finds broken links, redirect chains, duplicate pages, and other technical issues. It’s a must-have, especially for large sites where manual checks aren’t realistic.
Ahrefs Site Audit
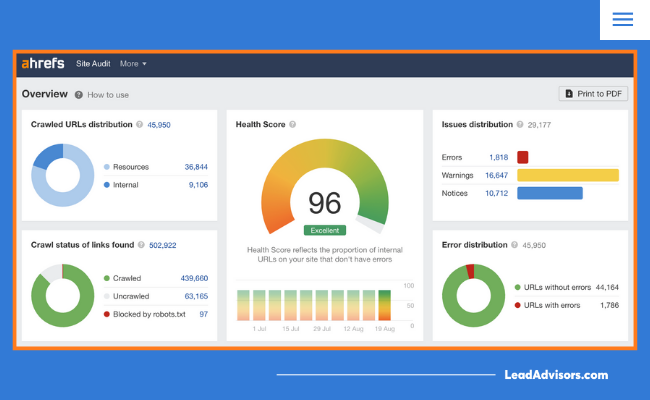
Ahrefs gives you a full view of your internal link structure. It helps you see which pages aren’t getting enough internal links, where crawl problems might be happening, and whether your URLs are being used consistently.
Sitebulb
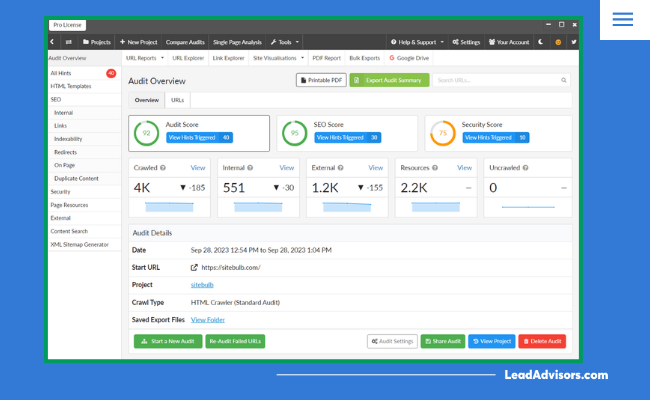
Sitebulb shows your links visually so you can see how everything connects. It’s great for spotting orphaned pages, deep pages, or links buried too far in your structure.
Google Search Console
Don’t overlook GSC. It tells you what Google sees:
- The Coverage Report shows what’s indexed and what’s not.
- The Crawl Stats Report shows how often Googlebot visits your pages.
- The Inspect URL Tool lets you check how Google views a specific page, including how it handles internal links.
What these tools help you do
- Find broken links before they hurt rankings or user experience.
- Spot inconsistent use of absolute and relative URLs
- Catch crawl issues that might be blocking key pages from getting indexed.
When your links are clear and your structure is solid, search engines can move through your site faster, and users can find what they need without friction. These tools help you make that happen.
Recommendation: When to Use Absolute vs. Relative Links
Both absolute and relative links have their place—it really depends on how your site is set up and what your SEO goals are.
Absolute URLs are usually the safer option when it comes to SEO. They give search engines a clear, complete path to your pages, help avoid duplicate content issues, and are the standard for things like sitemaps and backlinks.
Relative URLs are more flexible, which makes them great for internal linking during development, testing, or staging. They adjust based on where the page sits in your site’s structure, so you don’t have to rewrite links when things shift around.
The key is to pick the format that fits your setup and stick with it. Consistency across your site keeps things running smoothly and avoids unnecessary SEO headaches down the road.














